Figure 2.
A Conditional Point Mutant System to Inactivate PRC1 Catalysis
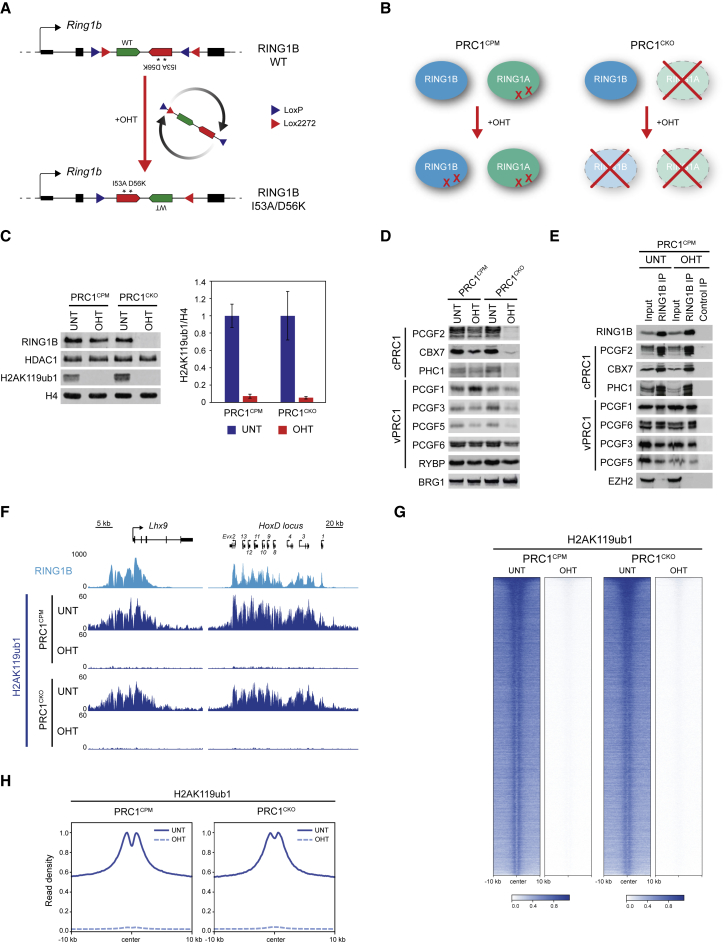
(A) A schematic of the engineered Ring1b locus in the PRC1CPM system before and after OHT addition.
(B) A schematic of the PRC1CPM and PRC1CKO ESCs.
(C) Western blot analysis of RING1B (with HDAC1 as a loading control) and H2AK119ub1 (with H4 as a loading control) in untreated and OHT-treated PRC1CPM and PRC1CKO cells (left panel). Quantification of H2AK119ub1 levels relative to histone H4. Error bars show SEM (n = 4) (right panel).
(D) Western blot analysis of cPRC1- and vPRC1-specific subunits in untreated and OHT-treated PRC1CPM ESCs (with BRG1 as a loading control).
(E) Immunoprecipitation of RING1B from untreated and OHT-treated PRC1CPM ESCs followed by western blot for cPRC1 and vPRC1 components. Western blot for EZH2 (a PRC2 component) was used as a negative control. For OHT-treated PRC1CPM ESCs, a control IP was performed with an isotype control antibody.
(F) Genomic snapshots of classical RING1B-bound loci, showing cChIP-seq for RING1B in wild-type cells and H2AK119ub1 in PRC1CPM and PRC1CKO cells.
(G) Heatmap analysis of H2AK119ub1 cChIP-seq at RING1B-bound sites in PRC1CPM and PRC1CKO cells. Genomic regions were sorted as in Figure 1E.
(H) Metaplot analysis of data shown in (G).
See also Figure S2.