Figure 1.
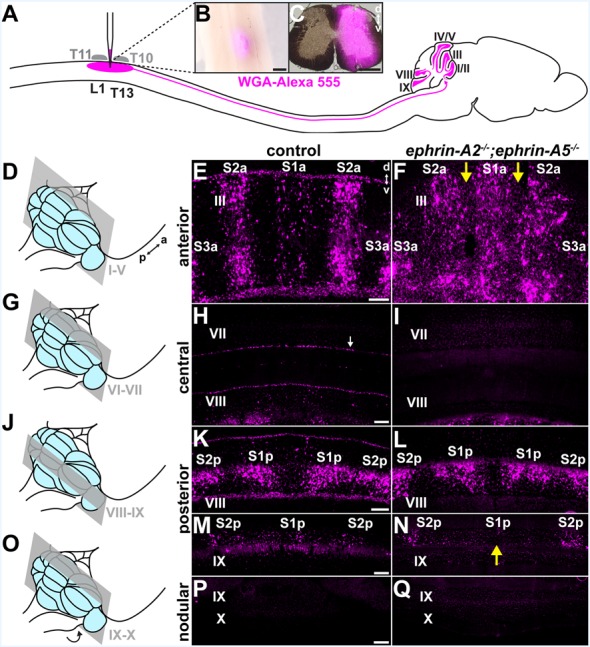
Spinocerebellar mossy fiber patterning is disrupted in ephrin-A2−/−;ephrin-A5−/− mice. (A) Strategy for labeling spinocerebellar mossy fiber terminals in the cerebellar cortex of ephrin-A2−/−; ephrin-A5−/− double knockout mice and control mice. We injected wheat germ agglutinin conjugated to Alexa fluorophores (WGA-Alexa 555) into the lower thoracic-upper lumbar spinal cord. Based on the curvature of the spine, we used vertebral segments T10 and T11 as landmarks to inject tracer into the underlying spinal cord segments of T13 to L1 (Harrison et al., 2013). (B) Whole-mount image of a dorsal view of a lower thoracic-upper lumbar spinal cord. A fluorescent image is overlaid on a bright-field image. The WGA-Alexa 555 tracer injection site is visible just lateral to the midline. a, anterior; p, posterior. Scale = 500 μm. (C) The A coronal section adjacent to a large injection site located in the lower thoracic-upper lumbar spinal cord. A fluorescent image is overlaid on a bright-field image. d, dorsal; v, ventral. Scale = 500 μm. (D) Schematic depicting a mouse brain with the cerebellum highlighted in blue and a coronal section through lobules I-V highlighted in gray. (E) Image of the WGA-Alexa 555 signal in the anterior cerebellum of a control mouse (N = 6). A midline parasagittal zone (S1a) and two zones lateral to the midline (S2a and S3a) are visible in lobule III. d, dorsal; v, ventral. Scale = 100 μm. (F) Image of the WGA-Alexa 555 signal in spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the anterior cerebellum of an ephrin-A2−/−;ephrin-A5−/− double knockout mouse (N = 6). The boundaries of S1a and S2a in lobule III are less defined, and territories of the granular layer that have a limited termination of spinocerebellar mossy fiber terminals in control mice contain ectopic spinocerebellar mossy fiber terminals (yellow arrows). (G) Schematic depicting a mouse brain with the cerebellum highlighted in blue and a coronal section through lobules VI-VII highlighted in gray. (H) Image after WGA-Alexa 555 tracing to test for spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the central cerebellum of a control mouse (N = 6). Spinocerebellar mossy fiber terminals are not present in lobule VII. The background staining in the Purkinje cells is likely due to leakage of the WGA-Alexa 555 tracer from the cerebrospinal fluid that accumulates from the injection in the spinal cord (Sillitoe et al., 2010; white arrow). Scale = 100 μm. (I) Image after tracing to test for WGA-Alexa 555 signal in spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the central cerebellum of an ephrin-A2−/−;ephrin-A5−/− double knockout mouse (N = 6). Spinocerebellar mossy fibers are not present in lobule VII. (J) Schematic depicting a mouse brain with the cerebellum highlighted in blue and a coronal section through lobules VIII and IX highlighted in gray. (K) Image of the WGA-Alexa 555 signal in spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the posterior cerebellum of a control mouse (N = 6). Two symmetrical pairs of parasagittal zones are visible in lobule VIII (S1p and S2p). Scale = 100 μm. (L) Image of the WGA-Alexa 555 signal in spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the posterior cerebellum of an ephrin-A2−/−;ephrin-A5−/− double knockout mouse (N = 6). The two symmetrical pairs of parasagittal zones in lobule VIII are visible and relatively well-defined (S1p and S2p). (M) Image of the WGA-Alexa 555 signal in spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the posterior cerebellum of a control mouse (N = 6). A midline parasagittal zone and a zone lateral to the midline are visible in anterior lobule IX (S1p and S2p). Scale = 100 μm. (N) Image of the WGA-Alexa 555 signal in spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the posterior cerebellum of an ephrin-A2−/−;ephrin-A5−/− double knockout mouse (N = 6). The midline parasagittal zone (S1p) and the zone lateral to the midline (S2p) are visible in anterior lobule IX. However, the S1p zone terminals are poorly organized compared to those in control mice (yellow arrow). (O) Schematic depicting a mouse brain with the cerebellum highlighted in blue and a coronal section through the nodular cerebellum (lobules posterior IX–X) highlighted in gray. The arrow indicates that lobule X is located underneath the posterior cerebellum, out of view. (P) Image after WGA-Alexa 555 tracing to examine for spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the nodular cerebellum of a control mouse (N = 6). Spinocerebellar mossy fibers are not present in posterior lobule IX or lobule X. Scale = 200 μm. (Q) Image after WGA-Alexa 555 tracing to examine for spinocerebellar mossy fibers in the nodular cerebellum of an ephrin-A2−/−;ephrin-A5−/− double knockout mouse (N = 6). Spinocerebellar mossy fibers are not present in posterior lobule IX or lobule X.
