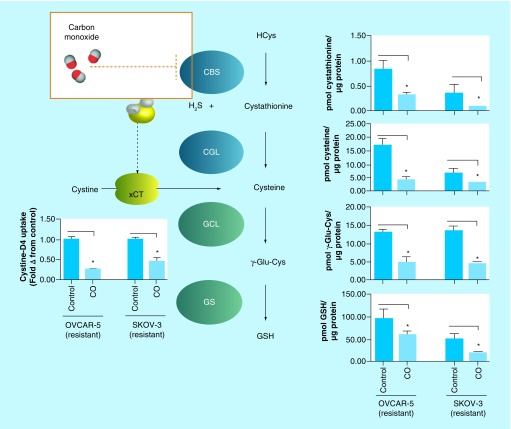
Figure 7. . Effect of carbon monoxide on transsulfuration/glutathione biosynthesis pathway metabolites, assayed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines, 24 h post-treatment.
CO inhibits cystathionine β-synthase, decreasing cystine uptake via the xCT and lowering steady state levels of cystathionine, the substrate for cystathionine γ-lyase. Consequently, CO decreases intracellular cysteine levels to inhibit glutathione biosynthesis as measured by steady state levels of γ-Glu-Cys and GSH, products of GCL and GS, respectively. Data representative of at least n = 3 individual experiments.
*p< 0.05.
CBS: Cystathionine β-synthase; CO: Carbon monoxide; Cys: Cysteine; GCL: Glutamate–cysteine ligase; Glu: Glutamic acid; GS: Glutathione synthase; GSH: Glutathione; H2S: Hydrogen sulfide; xCT: Glutamate–cystine antiporter.