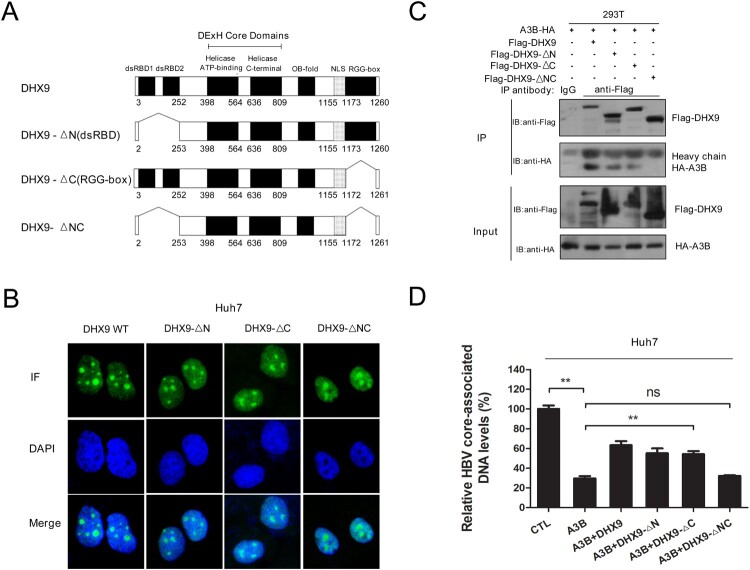
Figure 4.
DHX9 suppresses the anti-HBV function of A3B in a manner dependent on their interaction. (A) Schematic diagrams of full-length DHX9 and truncation mutants. dsRBD: double-stranded RNA binding domains; OB fold: oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding fold; NLS, nuclear localization signal; RGG, arginine-glycine-glycine; (B) Analysis of the localization of DHX9 wild-type (WT) and truncation mutants in Huh7 cells by immunofluorescence. (C) Mapping of the DHX9 domain required for the DHX9/A3B interaction. Lysates harvested from HEK293T cells cotransfected with HA-A3B and Flag-DHX9 wild-type (WT) or truncation mutants were used for co-IP. (F) DHX9 attenuates the anti-HBV function of A3B in a DHX9/A3B interaction-dependent manner. Huh7 cells were cotransfected with HA-A3B and Flag-DHX9 WT or truncation mutants, and viral DNA levels were measured by qPCR. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns, not significant.).