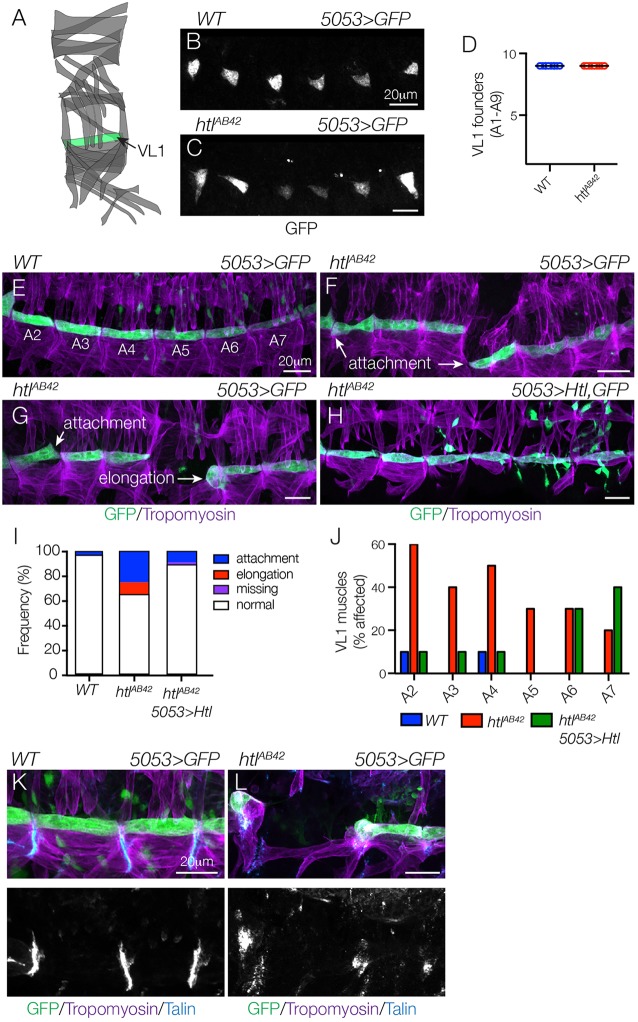
Fig. 2.
Htl acts cell autonomously to direct myotube guidance. (A) Diagram of the body wall muscles in a single embryonic segment (A2-A7), with 5053.Gal4-expressing VL1 muscle shown in green. (B-D) Stage 12 5053>eGFP embryos labeled for GFP to visualize VL1 nascent myotubes. The number of nascent myotubes specified in WT (B) and htlAB42 (C) embryos was equivalent (D). (E-H) Stage 16 5053>eGFP embryos labeled for GFP (green) and Tropomyosin (violet). WT VL1 muscles showed a largely invariant morphology (E). htlAB42 VL1 muscles often attached to the wrong muscle attachment site or failed to elongate (F,G). htlAB42 VL1 muscles that expressed Htl showed normal morphology (H). Mononucleate cells are visceral mesoderm cells that express 5053.Gal4. (I) Histogram of muscle phenotypes in Stage 16 embryos (n=60 per genotype). (J) Histogram of muscle phenotypes in Stage 16 embryos by embryonic segment (n=60 per genotype). (K,L) WT (K) and htlAB42 (L) stage 16 5053>eGFP embryos labeled for Talin (blue), GFP (green) and Tropomyosin (violet). htlAB42 VL1 muscles that failed to elongate will form myotendinous junctions. Embryos are oriented with anterior to the left and dorsal to the top.