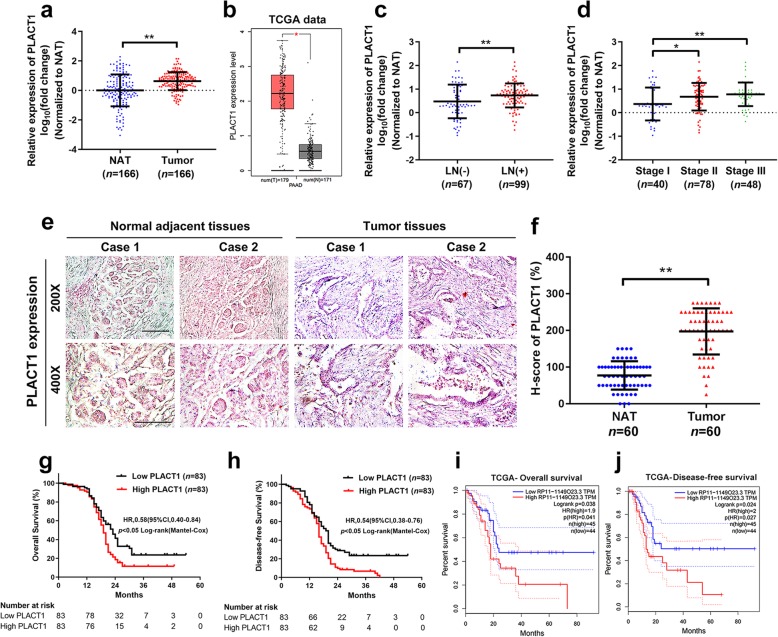
Fig. 1.
PLACT1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis of PDAC. a The expression of PLACT1 in human PDAC tissues (n = 166) paired with normal adjacent tissues (n = 166) were quantified by qRT-PCR analysis. The results were determined by nonparametric Mann–Whitney U-test. b TCGA and Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) data showed that PLACT1 is upregulated in PDAC tissues (n = 179) relative to non-tumorous tissues (n = 171). The nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test was used. c-d qRT-PCR assays evaluated the correlation of PLACT1 expression in human PDAC tissues (n = 166) with LN status (c) and tumor stages (d). The results were determined by nonparametric Mann–Whitney U-test. e-f ISH analysis of PLACT1 expression (blue) in the paraffin-embedded NAT (n = 60) and tumor sections of PDAC (n = 60). Representative images (e) from two clinical cases and H-score (f) are shown. Statistical significance was assessed by χ2 test. Scale bars: 50 μm. g-h The Kaplan–Meier curves represented overall survival (g) and disease-free survival (h) of PDAC patients with low vs. high expression of PLACT1. The cutoff value was the median expression of PLACT1. i-j PDAC patients from the TCGA data were divided into low and high PLACT1expression groups; overall survival (i) and disease-free survival (j) of the patients in the groups used Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. p-values was calculated by the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01