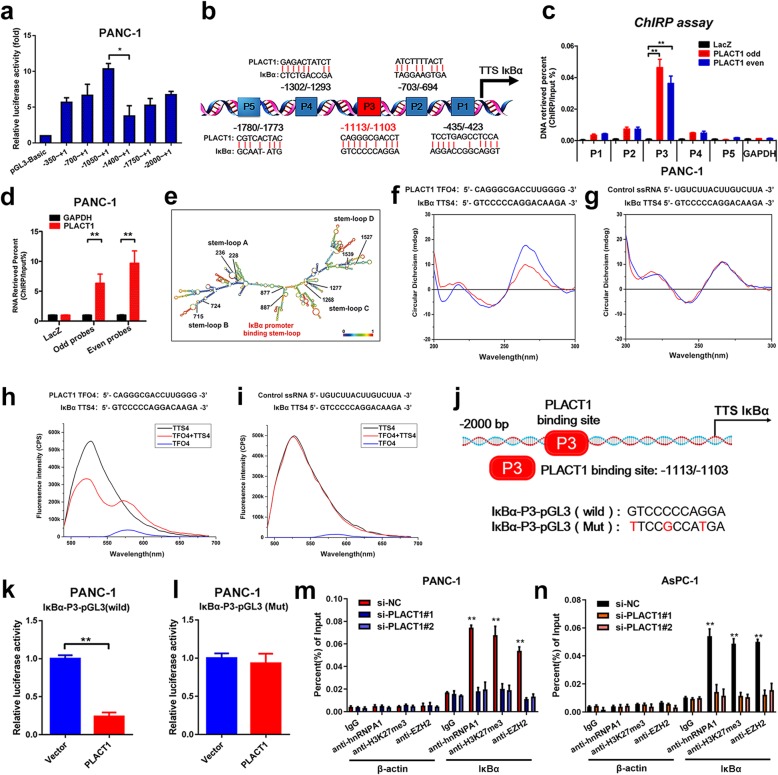
Fig. 7.
PLACT1 forms triplexes with the promoter of IκBα and downregulates IκBα expression. a Luciferase reporter assays and sequential deletions detect transcriptional activity of the IκBα promoter. b Schematic images of the potential PLACT1 binding sites in the IκBα promoter. c-d ChIRP analysis of PLACT1-associated chromatin in PANC-1. Retrieved chromatin and RNA were assessed by qRT-PCR. ePLACT1 is predicted to have 5 stable stem-loop structures (http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/). The red text indicates the IκBα promoter binding stem-loop structures in PLACT1. f-g CD spectroscopy of the mixture (blue) and the sum (red) of TFO in PLACT1 and TTS in the IκBα promoter sequences are shown (f). Control ssRNA/ IκBα is used as negative control (g). h-i FRET of TFO in PLACT1 (black), TTS in the IκBα promoter sequences (blue), and their mixture (red) are shown (h). Control ssRNA/ IκBα is used as negative control (i). j IκBα promoter with mutated PLACT1 binding sites and wild-type IκBα promoter were cloned into pGL3-luc reporter vector. k-l, Dual-Luciferase reporter assays were performed to analyze IκBα promoter with wild-type (k) and mutated PLACT1 binding site IκBα promoter (l). m-n ChIP-qPCR analysis of hnRNPA1, EZH2 occupancy and H3K27me3 status in the IκBα promoter after knockdown of PLACT1 in PANC-1 (m) and AsPC-1 (n) cells. Statistical significance was calculated by using two-tailed t-tests and ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s tests for multiple comparison. The error bars represent triplicate standard deviations. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01