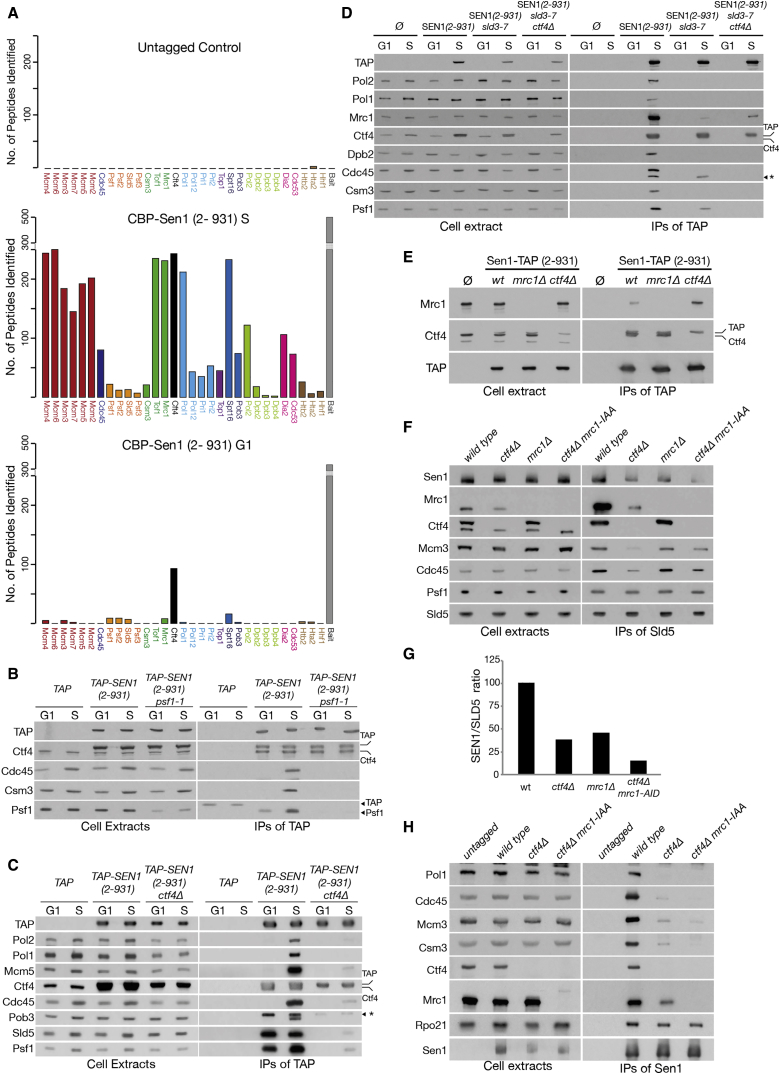
Figure 2.
Sen1 Binds the Replisome Components Ctf4 and Mrc1
(A) MS analysis of the proteins co-purifying with Sen1 (2–931) was conducted in S and G1 phases.
(B) IB analysis of the proteins IPed with Sen1 (2–931) and an empty control in strains carrying the PSF1 or psf1-1 allele. Cells were arrested in G1, shifted to 37°C for 1 h (G1), and then released into S phase for 20 min at 37°C (S).
(C) Sen1 (2–931) binding of GINS in G1 depends on Ctf4. IB analysis of the proteins IPed with Sen1 (2–931) and an empty control, with or without CTF4. Cells were arrested in G1 and released in S phase for 20 min at 30°C. Ctf4 and TAP-Sen1 (2–931) have similar sizes and run closely in gel electrophoresis.
(D) IB analysis of the proteins interacting with TAP-Sen1 (2–931) in the presence or absence of origin firing and CTF4. Cells were treated as described in Figure S2B. G1 samples were collected before galactose induction.
(E) Wild-type, mrc1Δ, or ctf4Δ cells expressing TAP-Sen1 (2–931) were arrested in G1. IB analysis of cell extracts and IPs is shown.
(F) Wild-type, ctf4Δ, mrc1Δ, and ctf4Δ mrc1-AID strains were arrested in G1, treated for 1 h with 0.5 mM auxin indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) final concentration, and released in S phase. IB analysis of cell extracts and IPs is shown.
(G) Quantification of the relative signal of Sen1-9MYC versus the TAP-Sld5 signal, normalized against the wild type.
(H) Experiments were conducted as in (F). Wild-type, ctf4Δ, and ctf4Δ mrc1-AID strains, carrying an untagged or a SEN1-TAP allele, were used. Asterisk indicates a non-specific band.