Figure 4. 3D antibiotic scaffolds reduce blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability associated with S. aureus craniotomy infection.
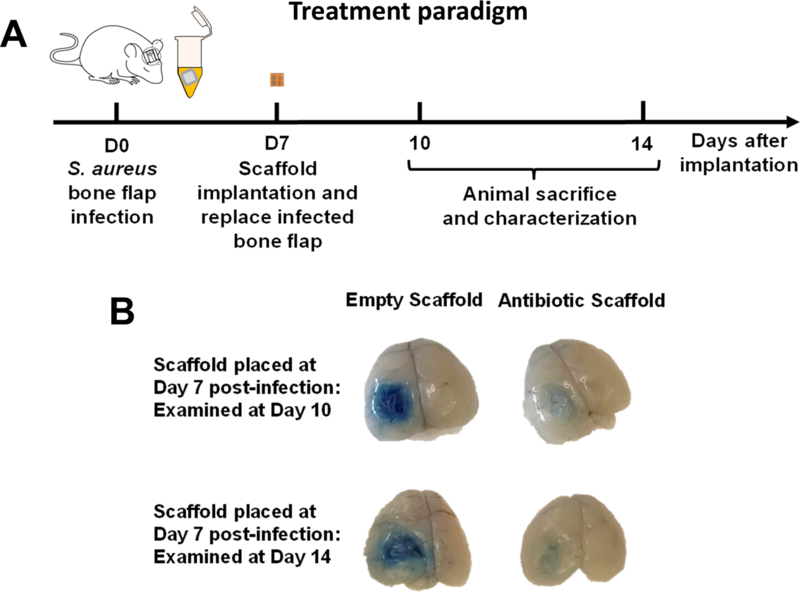
(A) Schematic depicting the paradigm used to assess the treatment efficacy of 3D bioprinted scaffolds. (B) 3D antibiotic scaffolds (daptomycin + rifampin) were inserted at day 7 after S. aureus craniotomy infection, whereupon BBB permeability was assessed 3 or 7 days later using Evan’s blue. Results are representative of 5 mice per group.
