Figure 6. Efficacy of 3D bioprinted antibiotic scaffolds to prevent S. aureus craniotomy-associated infection.
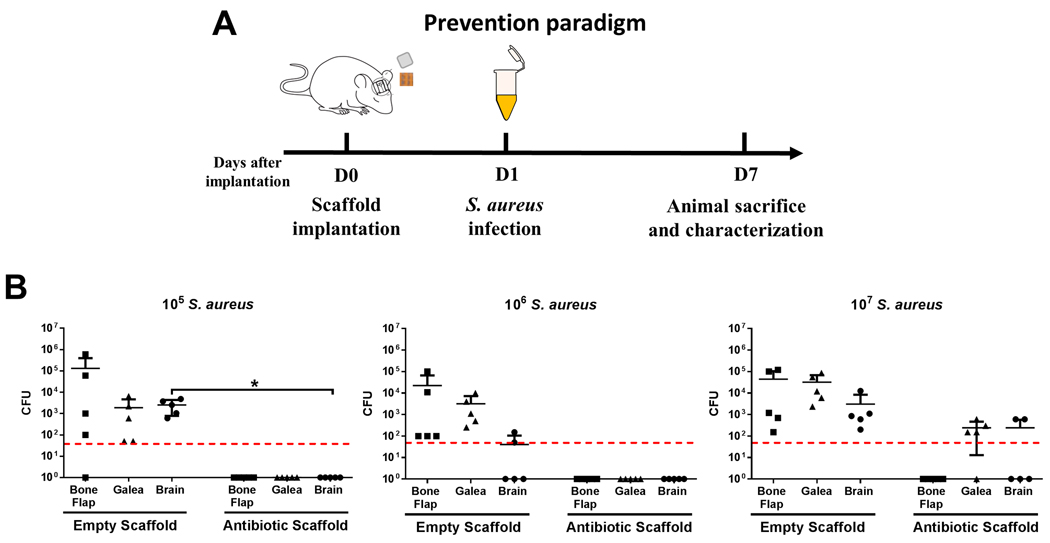
(A) Schematic depicting the experimental paradigm to assess the ability of 3D bioprinted scaffolds to prevent S. aureus craniotomy infection. (B) 3D bioprinted scaffolds ± antibiotics (daptomycin + rifampin) were placed at the time of craniotomy, whereupon mice (n=5 per group) where challenged 1 day later with 105−107 CFU live S. aureus at the surgical site. Bacterial burdens were determined 7 days later. Results were analyzed by an unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction (*, p < 0.05).
