Figure 1.
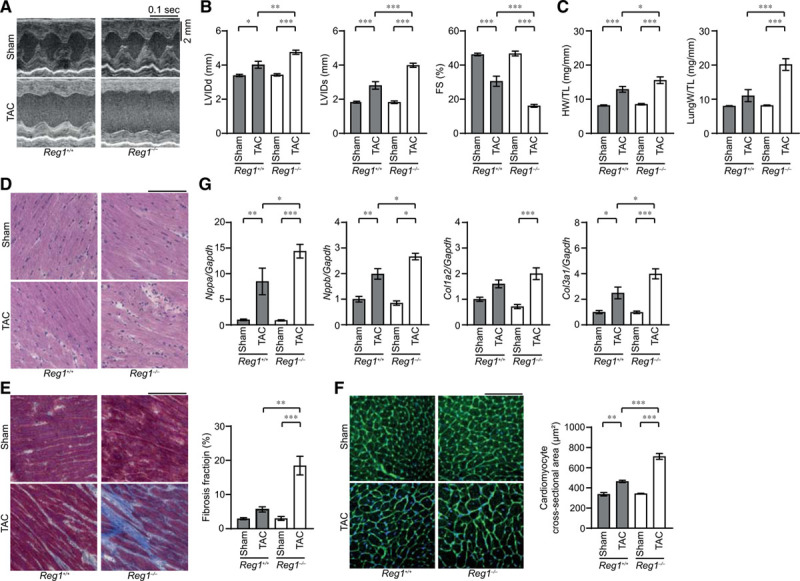
Pressure overload–induced cardiomyopathy in Reg1-/- mice. The Reg1+/+ and Reg1−/− mice were subjected to pressure overload by means of transverse aortic constriction (TAC). The mice were analyzed 4 weeks after TAC. Data were evaluated by 1-way analysis of variance with the Bonferroni post hoc test. Data are mean ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. A, M-mode echocardiographic tracings from sham- or TAC-operated Reg1+/+ or Reg1−/− mice. B and C, Echocardiographic (B) and physiologic (C) parameters. Total n=7 (sham–Reg1+/+), 7 (TAC–Reg1+/+), 7 (sham–Reg1−/−), or 6 (TAC–Reg1−/−) per group. D through F, Hematoxylin-eosin–stained (D), Masson trichrome–stained (E), and wheat germ agglutinin–stained (F) heart sections. Scale bar, 100 µm. Fibrosis fraction was measured (n=3). Cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area was measured by tracing the outline of 70 myocytes in the nonfibrotic area in each section (n=3). G, mRNA expression of Nppa, Nppb, Col1a2, and Col3a1. Total n=5 (sham–Reg1+/+), 4 (TAC–Reg1+/+), 5 (sham–Reg1−/−), or 5 (TAC–Reg1−/−) per group. Gapdh mRNA was used as the loading control. The averaged value in sham-operated Reg1+/+ hearts was set equal to 1. FS indicates fractional shortening; HW/TL, heart weight/tibia length; LungW/TL, lung weight/TL; LVIDd, end-diastolic left ventricular internal dimension; and LVIDs, end-systolic left ventricular internal dimension.
