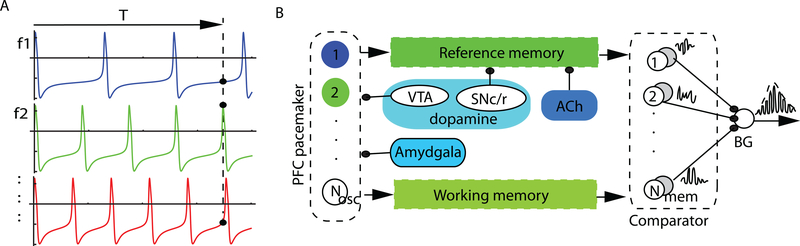
Figure 2. The striatal beat frequency model.
(A) All frontal cortex oscillators start in phase at the beginning of interval timing test but fire with different frequencies f1, f2, f3, … in the alpha band [8, 13] Hz. At the criterion time, T, the states (phases) of all oscillators (the solid dots along the vertical dashed line at T) are stored in the long-term (reference) memory. The comparator block (loosely associated with the basal ganglia) compares the current state of oscillators (working memory) against the content of the reference memory and generates a strong response if they coincide. (B) The oscillators are connected both with the reference and the working memory, which in turn provide input to the comparator. The SBF-ML model implemented also cholinergic and dopamine modulations. Emotional stimuli have the ability to reset the frontal cortex oscillators, presumably through amygdala link to frontal cortex (this is not shown in the figure). FC: frontal cortex; BG: basal ganglia; SNc/r: substantia nigra pars compacta/reticulata; VTA: ventral segmental area.