Fig. 4. Characterization of ARN23765 in bronchial epithelial cells.
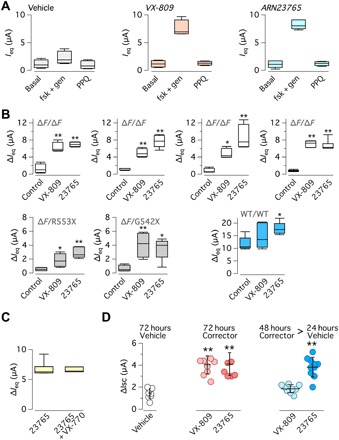
(A) Examples of data obtained with the TEEC/PD technique. Graphs show the values of short-circuit current equivalent (Ieq) calculated from TEEC and PD under basal conditions (already containing amiloride), with forskolin (fsk; 20 μM) plus genistein (gen; 50 μM), and after block with PPQ102 (PPQ; 30 μM). Before measurements, cells were treated for 24 hours with vehicle, VX-809 (1 μM), or ARN23765 (10 nM). Data are from four to six experiments. (B) TEEC/PD data obtained with vehicle, VX-809 (1 μM), and ARN23765 (10 nM) on cells from four different patients with F508del/F508del, two patients with F508del/other mutation, and a non-CF individual. The box plot graphs report ∆Ieq, i.e., the amplitude of the effect of PPQ102. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test; n = 5 to 6). (C) Chronic treatment of F508del/F508del bronchial epithelial cells with VX-770 (1 μM) plus ARN23765 (10 nM) for 24 hours. For comparison, cells were treated with ARN23765 alone. After treatment, cells were acutely stimulated with forskolin plus genistein as done for the others TEEC/PD experiments. F508del-CFTR activity, measured as ∆Ieq with the TEEC/PD technique, showed no differences between the two conditions (n = 6). (D) Persistence of ARN23765 corrector effect. F508del/F508del bronchial epithelial cells were treated with VX-809 (1 μM) or ARN23765 (1 nM), for 72 hours or for 48 hours followed by 24 hours without compound. F508del-CFTR activity was determined in short-circuit current recordings. **P < 0.01 (ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test).
