Fig. 1.3.
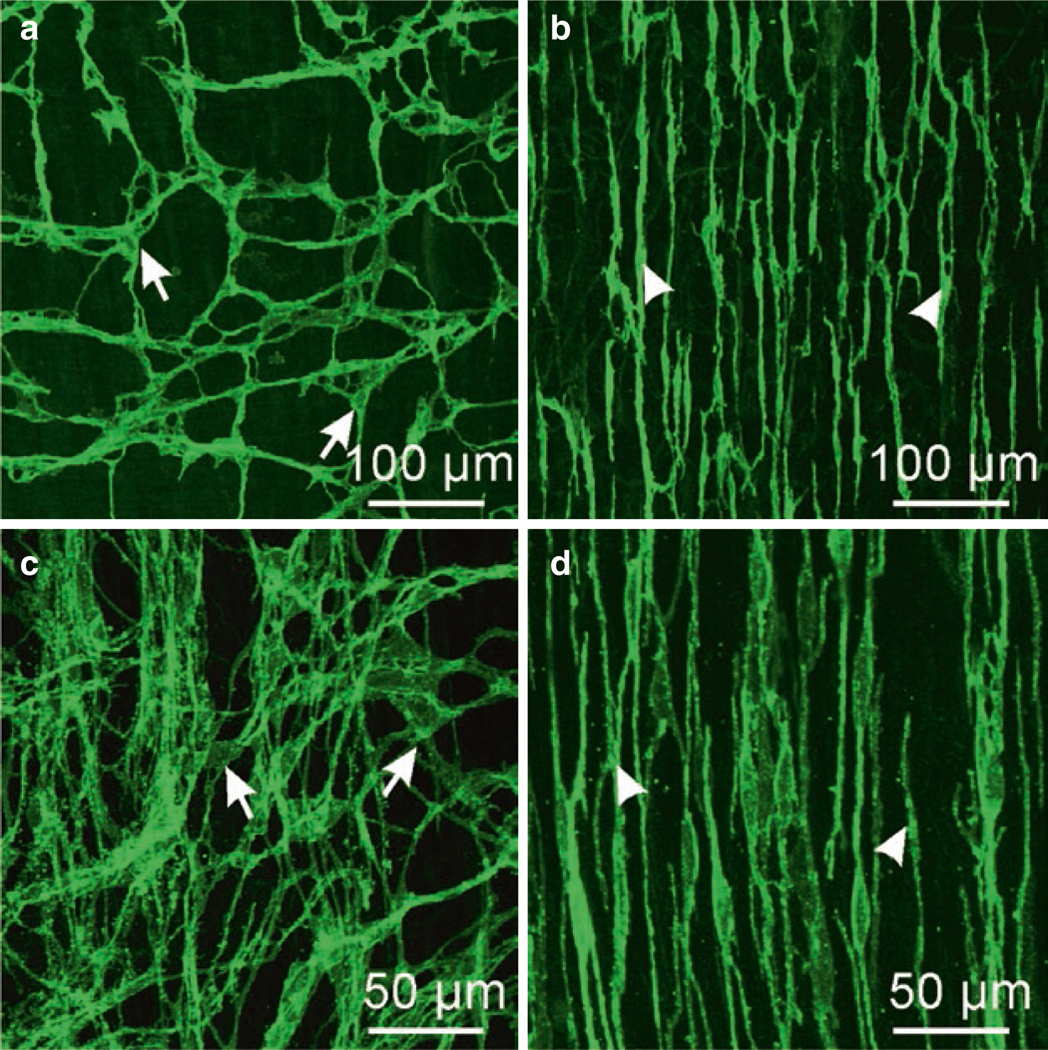
ICC in murine and monkey small intestine. (a, b) are whole mounts imaged by confocal microscopy of ICC-MY (a) labeled with anti-c-Kit antibody (arrows) and ICC-DMP (b; arrowheads) in murine small intestine. ICC-MY have multiple processes and form an extensive interconnected network via gap junction coupling between ICC and with adjacent SMCs. ICC-DMP run in parallel with the circular muscle fibers and are concentrated very close to the submucosal edge of the circular muscle layer in the mouse. ICC-DMP are closely associated with the processes of enteric motor neurons (not shown) and PDGFRα+ cells (not shown). (c, d) are images from the small intestine of Macaca fascicularis (cynomolgus monkey). ICC-MY (c; arrows) in this species also display a network of cells between the circular and longitudinal muscle layers and ICC-DMP (d; arrowheads) are also present near the submucosal surface of the circular muscle layer. Redrawn from [206]
