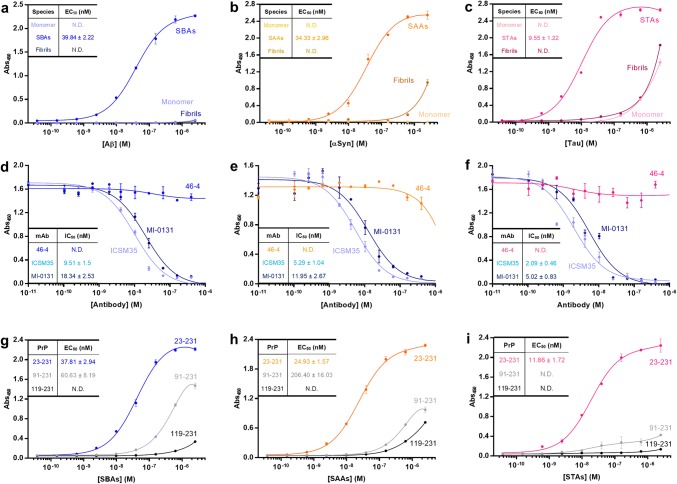
Fig. 2.
Soluble aggregates of Aβ, α-Synuclein and Tau bind to the N-terminus of PrP. a–c Binding of Aβ (a), αSyn (b) and tau (c) monomers, soluble aggregates and fibrils to immobilized PrP23–231 was assessed using an ELISA-like microtiter plate assay. Data shown are the mean ± SD from a single experiment, whereas inset EC50s are from at least four independent experiments. d–f Binding of soluble protein aggregates to immobilized PrP23–231 can be inhibited by anti-PrP monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to Sites I (MI-0131) and II (ICSM35), but not a nonspecific mAb (46–4). Data shown are the mean ± SD from a single experiment, whereas inset IC50s are from at least four independent experiments. g–i To determine the regions of PrP involved in binding soluble protein aggregates, PrP23–231, PrP91–231, and PrP119–231 were immobilized and binding of SBAs (g), SAAs (h) and STAs (i) measured. Data shown are the mean ± SD from a single experiment, whereas inset EC50s are from at least 4 independent experiments