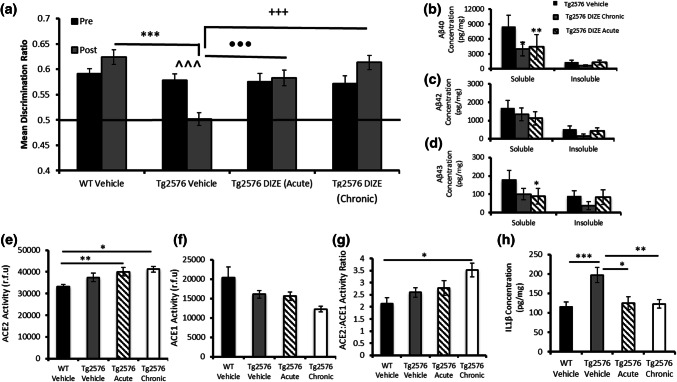
Fig. 6.
Acute and chronic administration of DIZE prevents the onset of cognitive impairment in young pre-symptomatic Tg2576 mice. a Associative recognition memory was assessed in younger WT (n = 20) and Tg2576 mice (9–12 months of age) that received either acute (10 days; n = 17) or chronic (10 weeks n = 11) DIZE administration. Tg2576 vehicle mice (n = 16) showed an age-dependent impairment in OiP performance (^^^p < 0.001), which was not observed in either the acute or chronic DIZE-administered Tg2576 mice (ps > 0.05). Tg2576 vehicle mice were also impaired compared to WT vehicle (***p < 0.001), Tg2576 acute (•••p < 0.001) and Tg2576 chronic DIZE administered mice (+++p < 0.001). b–d Aβ levels were quantified by ELISA. Soluble Aβ40 level was reduced in both chronic (*p < 0.05) and acute DIZE-administered Tg2576 mice (**p < 0.01) compared to Tg2576 vehicle mice. Soluble Aβ43 was reduced in Tg2576 mice that received acute DIZE administration (*p < 0.05) compared to Tg2576 vehicle mice. e–g ACE2 and ACE1 activities were determined by enzyme activity assays. ACE2 activity was significantly increased in the hippocampus of Tg2576 mice administered DIZE either acutely (**p < 0.01) or chronically (p < 0.05) compared to WT vehicle mice. Despite a numerical reduction in ACE1 activity in DIZE administered mice, no significant changes were reported, p > 0.05; however, the ratio of ACE2:ACE1 was significantly increased in Tg-chronic mice compared to WT vehicle (*p < 0.05). h IL-1β level was increased in Tg2576 vehicle mice compared to WT vehicle controls (***p < 0.001) but was significantly reduced after acute (*p < 0.05) and chronic (**p < 0.01) DIZE administration in Tg2576 mice compared to Tg vehicle mice. Behavioural data were analysed using mixed measures ANOVA. Significant interactions were further analysed by tests for simple main effects with Bonferroni corrections for multiple comparisons. ACE2 and IL-1β analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey analysis. Amyloid analysis was performed using non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. Error bars represent the SEM