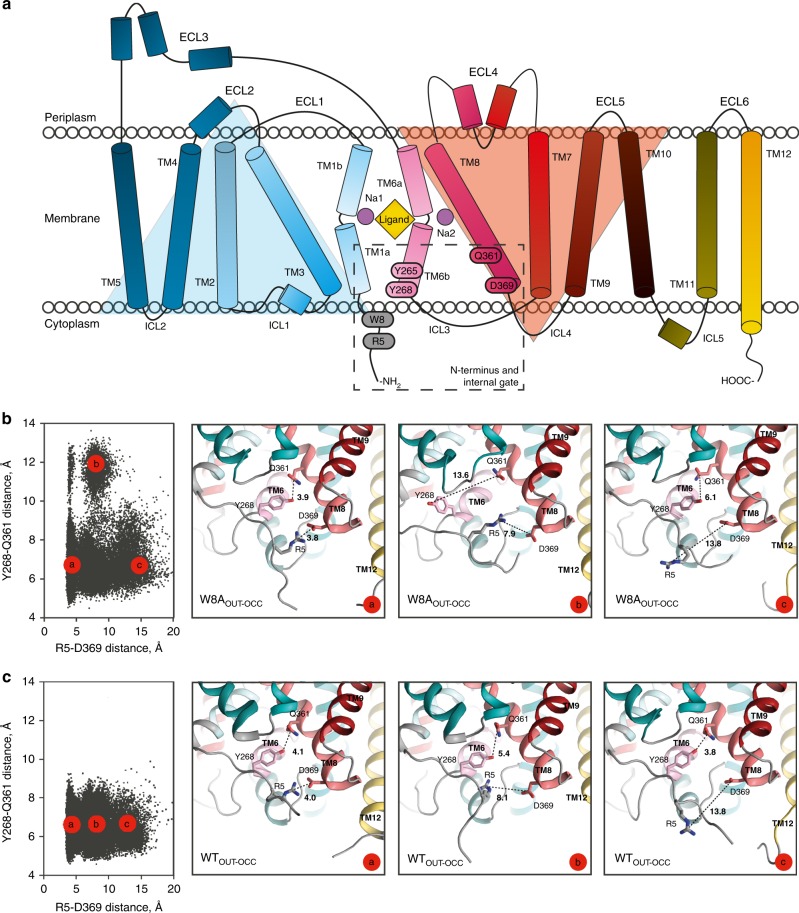
Fig. 2. Secondary structure of LeuT and conformational dynamics of the intracellular gate.
a Topology of the LeuT monomer with transmembrane segments (TMs) 1-12, extracellular loops (ECLs) 1–6 and intracellular loops (ICLs) 1–5. TMs 1–5 and TMs 6–10 are related by a pseudo two-fold rotation as highlighted by the light blue and orange triangles, respectively10. Dashed rectangular indicates region, including the N-terminal W8 residue and residues constituting the internal gate (R5, Y265, Y268, Q361, and D369). b Conformations of W8AOUT-OCC LeuT construct collected from the ~10-µs ensemble MD trajectories (run in 10 statistically independent replicates, each ~1-µs long) projected onto two-dimensional (2D) space of the R5-D369 and Y268-Q361 distances. Each black dot (left panel) represents one snapshot from the combined trajectories of the 10 replicas, collected at 800-ps intervals for a total of >10.000 points. The three right panels are structural representations of the system corresponding to the three microstates (“a”–“c”), highlighting various degrees of opening of the two gates. The structures show the protein (close-up of the gate residues R5, D369, Y268, and Q361) with the above-mentioned distances indicated. c Conformational dynamics of the intracellular gate of WTOUT-OCC LeuT construct. Both the 2D and corresponding structural representations are shown similarly to Fig. 2b.