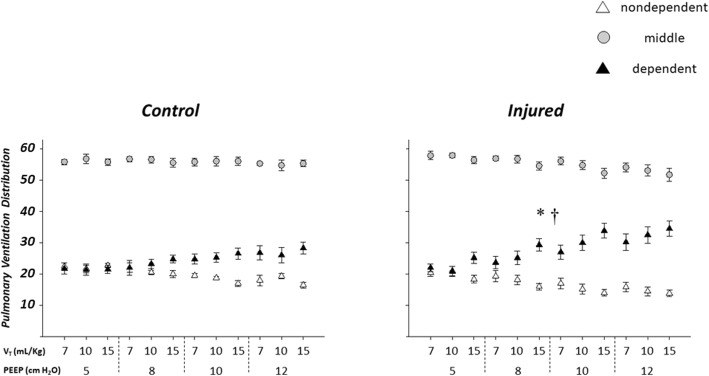
Fig. 4.
Regional distribution of pulmonary ventilation in the control (left, n = 4) and injured (right, n = 6) groups. Larger PEEP levels were associated with greater percent increase in the ventilation of the dependent lung in the injured group than in the control group. Similarly, larger VT was associated with a greater percent increase in dependent lung ventilation in the injured group than in the control group. * indicates greater percent increase in the ventilation of the dependent lung region with larger PEEP in the injured than in the control group; † indicates greater percent increase in the ventilation of the dependent lung region with larger VT in the injured than in the control group. PEEP = positive end-expiratory pressure. VT = tidal volume