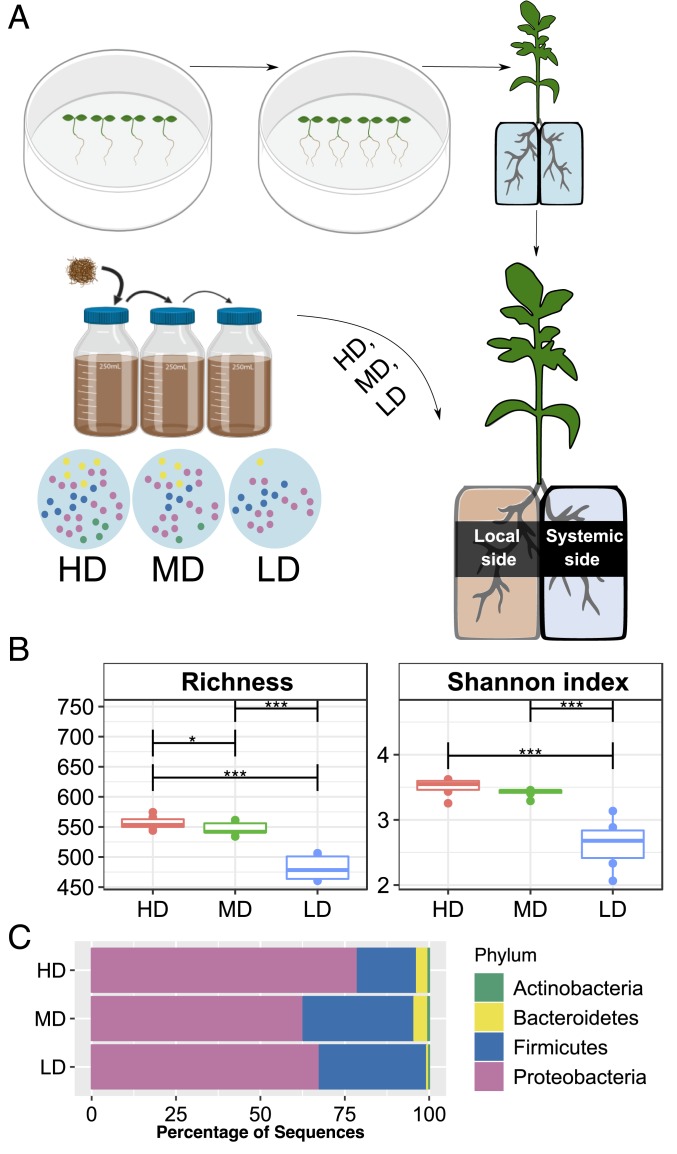
Fig. 1.
Linking local-side root microbiome diversity to the chemical composition of systemic root exudation. (A) Schematic representation of the split-root hydroponics experimental design. Local-side roots of the split-root set-up were inoculated with soil microbiome, established using the dilution-to-extinction approach; HD, MD, or LD diversity microbiomes and exudate samples were collected from the systemic side. (B) Alpha diversity indices of root microbiomes (local side) measured 7 d postinoculation. Number of species (richness) or Shannon index gradually decreased among HD, MD, LD microbiomes (asterisks denote difference in alpha diversity indices, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0005, ANOVA followed by Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) post hoc multiple comparison). (C) Bar plots of relative abundances of the top four phyla in each root microbiome (HD, MD, and LD) after 7 d of inoculation. Data are the average of six biological replicates. OTU abundance (97% similarity) and assigned taxonomic classifications used to construct this panel can be found in Dataset S1C. The bacterial relative abundance displayed at the phylum level for all individual samples can be found in SI Appendix, Fig. S3B.