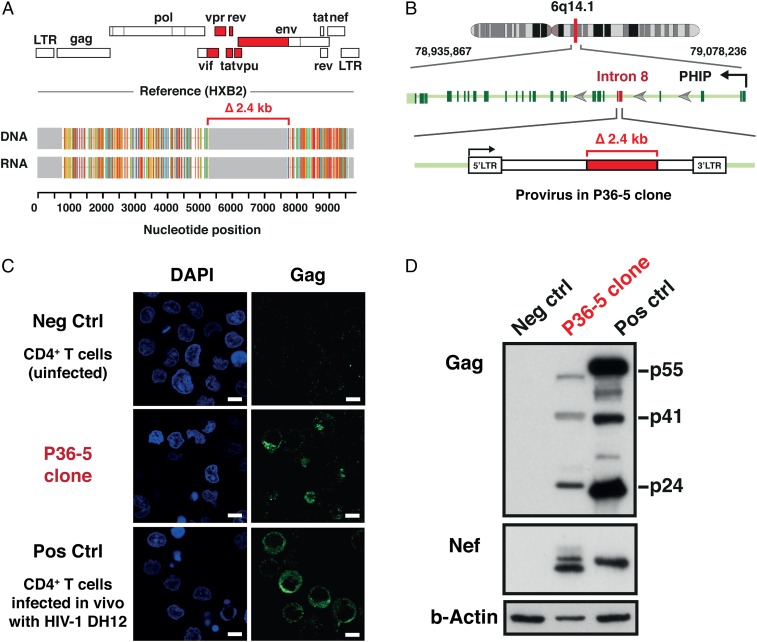
Fig. 4.
Expression of HIV-DNA, HIV-RNA, and HIV-1 proteins in the CD4+ T cell clone harboring a defective provirus derived from an HIV-infected individual during cART. (A) HIV-RNA sequences corresponded precisely to the HIV-DNA sequences for the P36-5 clone. Analysis of the genome structure revealed a 2.4-kb internal deletion affecting the region encoding the HIV-1 accessory proteins (tat, rev, vpu, and others) and the gp120 portion of the Env protein (red). The Gag, Pol, and Nef regions remained intact in the provirus present in the P36-5 clone. (B) Whole-genome sequencing confirmed the presence of two intact LTRs and revealed the provirus to be integrated in intron 8 of the PHIP gene in the opposite orientation to the PHIP gene. (C) Confocal microscopy analysis of the intracellular expression of the Gag p24 protein. A mouse monoclonal antibody for HIV-1 p24 (clone: 39/5.4A) was used. Nuclei were visualized by DAPI (blue). Original magnification was ×63. (Scale bars, 5 µm.) (D) Expression of HIV-1 proteins by Western blot. Negative control (Neg Ctrl), uninfected CD4+ T cells; and positive control (Pos Ctrl), CD4+ T cells infected in vitro with the DH12 strain of HIV-1. A mouse monoclonal antibody for HIV-1 p24 (clone: 39/5.4A) and a mouse monoclonal antibody for HIV-1 Nef (clone: 3A2) were used. The predicted sizes of the Nef proteins, based on the provirus sequences for DH12 and P36-5, were 23.4 kDa and 22.6 kDa, respectively. The higher molecular weight band seen for Nef in P36-5 likely represents posttranslational modifications such as myristoylation.