Fig. 2.
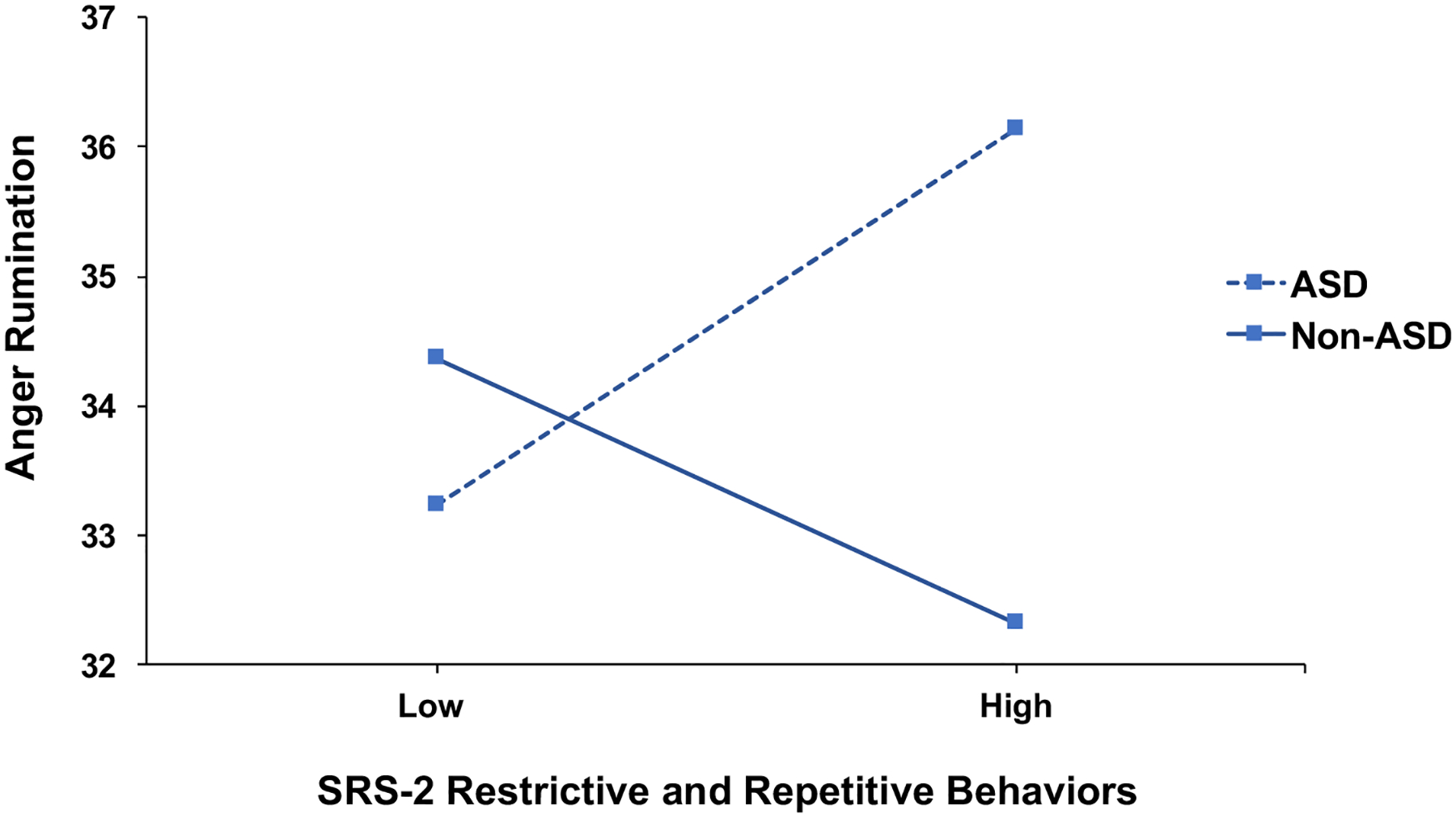
Interaction between ASD diagnosis and restricted and repetitive behaviors is associated with anger rumination in the total sample (N = 186). Restrictive and repetitive behaviors are measured using the social responsiveness scale-second edition (SRS-2) restricted and repetitive behaviors scale. Anger rumination is measured using the Anger Rumination Scale total score. The model controls for gender, aggression using the reactive–proactive aggression questionnaire total score, and the interaction between ASD diagnosis and aggression. High and low levels of restrictive and repetitive behaviors were dichotomized using a median split for visualization purposes. The total sample of participants includes children with ASD (n = 63), children with disruptive behavior disorder without ASD (n = 79), and healthy controls (n = 44)
