Fig. 1. Model for chromophore isomerization in FPs.
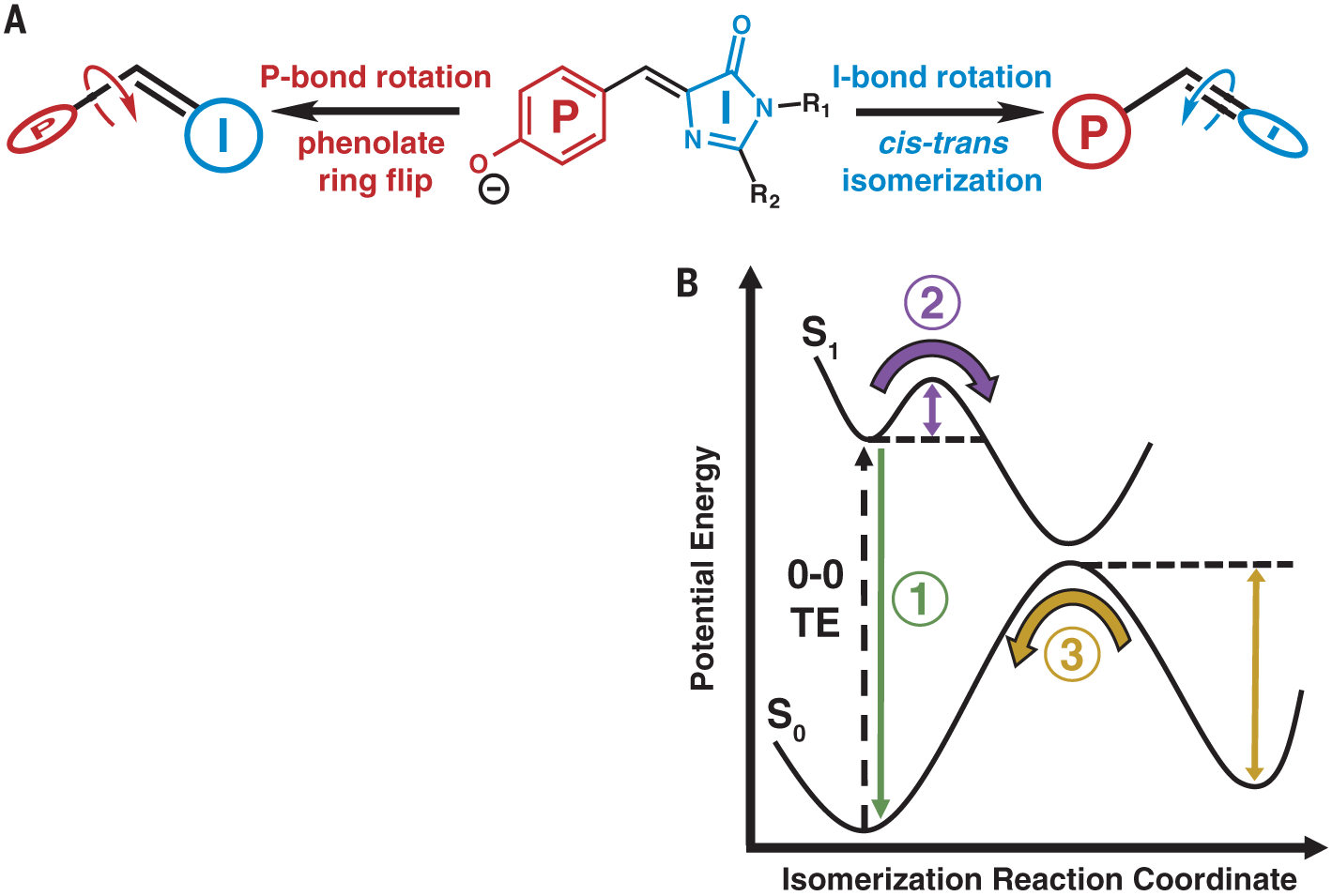
(A) Rotation can occur about either the P or I bond, leading to a P-ring flip or cis-trans isomerization, respectively. R1 and R2 represent residues Gly64 and Cys62, respectively, which covalently link the chromophore to the rest of the FP (Fig. 2A). (B) General potential energy diagram along the isomerization reaction coordinate for a photoisomerizable chromophore. 0–0 TE represents the TE between the lowest vibrational state of the ground and excited electronic states. Three features studied in this work are emphasized: fluorescence (1, green), ES barrier crossing (2, purple), and GS barrier crossing (3, yellow).
