FIG 8.
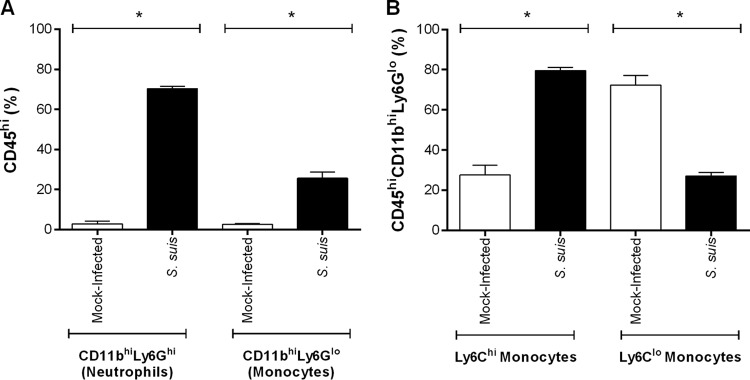
S. suis induces the infiltration of neutrophils, and to a lesser extent of inflammatory monocytes, into the central nervous system (CNS) following infection. Infiltrating CD45hiCD11bhiLy6Ghi neutrophils and CD45hiCD11bhiLy6Glo monocytes in the CNS of mock-infected and S. suis-infected mice (upon presentation of clinical CNS disease) were analyzed using flow cytometry (A). Inflammatory (Ly6Chi) and patrolling (Ly6Clo) monocyte subpopulations (B) were determined by gating on the CD45hiCD11bhiLy6Glo monocytes in panel A. The data represent the mean ± SEM (n = 3). * (P < 0.05) indicates a significant difference between mock-infected and S. suis-infected mice as determined using the Mann-Whitney rank sum test.