Figure 6. Inhibition of Wnt3a aggravates TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses and enhances neutrophil infiltration in the murine model of endotoxic shock.
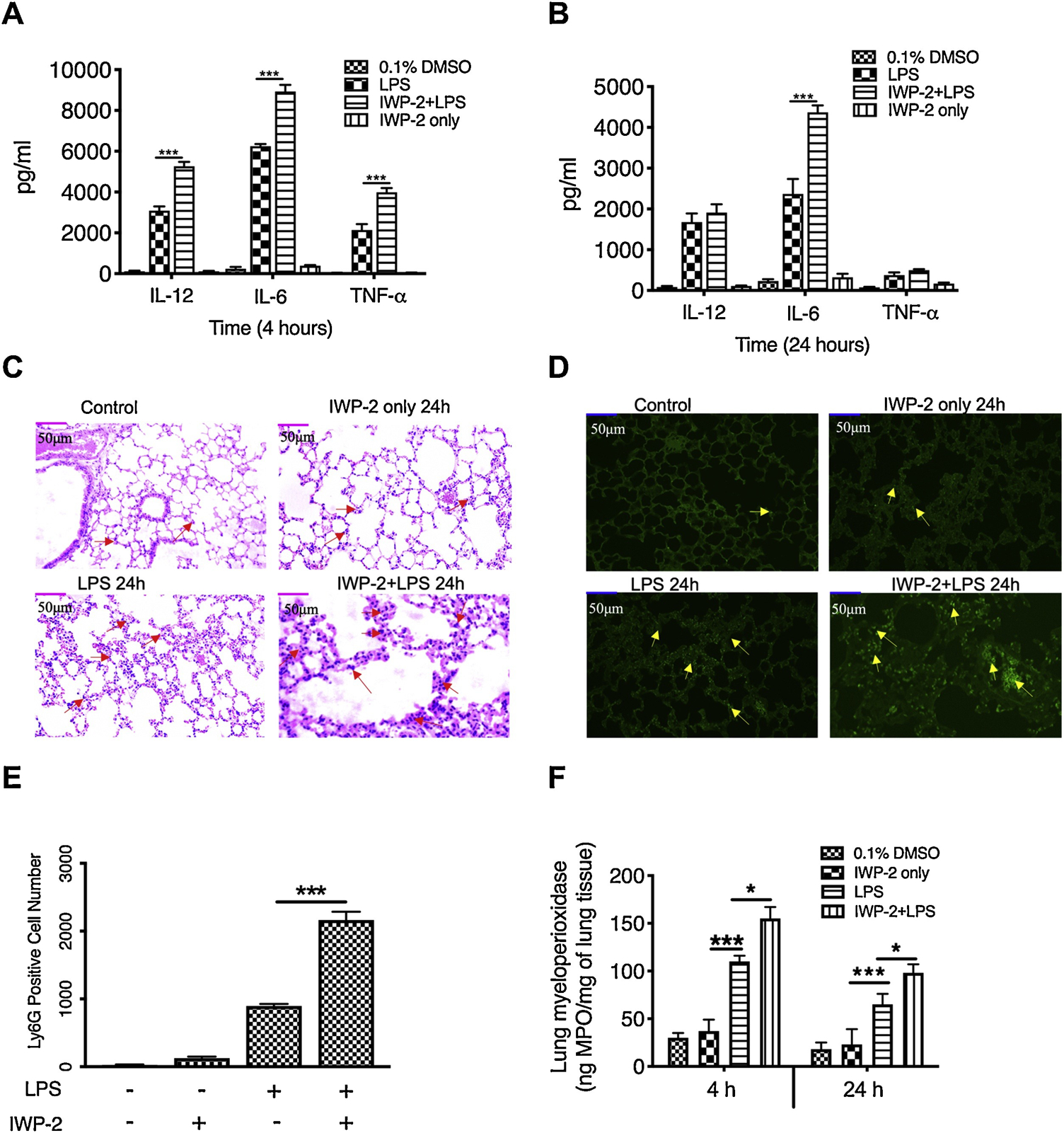
IL-12P40, IL-6 and TNFα levels at 4 hours (A) or 24 hours (B) post-injection of LPS in C57BL/6 mice with or without IWP-2 (15mg/kg) pretreatment. (C) H&E staining of serial section of lung from mice injected with PBS (Control), IWP-2, LPS, or LPS plus IWP-2 for 24 hours showing the infiltration of inflammatory cells (area with red arrows) and tissue damage (×20 magnification). (D) Polymorphonuclear neutrophil infiltration was assessed by staining tissue section of lung with FITC-conjugated Ly6G (yellow arrow; magnification, ×20). (A)-(B) and (C)-(D) are separate, and each group has a total of 6 mice for analysis. (E) Levels of infiltrated neutrophils presented by the average number of Ly6G-positive cells in 5 different views. (F) The amount of myeloperoxidase in lung tissues at 4 h and 24 h after different treatments. Data represent the arithmetic means±SD of 3 biological replicates. “*” and “***” indicate statistically significant at P<0.05 and P<0.001, respectively. Data represent the arithmetic mean±S.D. of three biological replicates.
