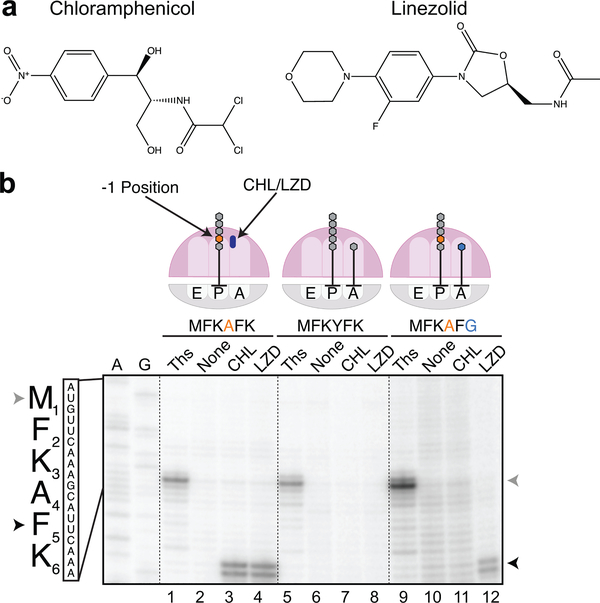
Figure 1. Context-specific inhibition of translation by chloramphenicol and linezolid.
a. Chemical structures of antibiotics chloramphenicol (CHL) and linezolid (LZD). b. In vitro toeprinting analysis of CHL- or LZD-induced translational arrest on three different mRNA constructs (complete sequences of the templates are shown in Supplementary Fig 1; independently repeated at least twice with similar results). The toeprint bands produced by CHL- or LZD-arrested ribosomes at the F5 codon of the mRNAs are indicated by black arrowheads. Gray arrowheads show the toeprint bands produced by ribosomes stalled at the start codons due to the presence of thiostrepton (Ths). Sequencing lanes A and G for the MFKAFK template are shown.