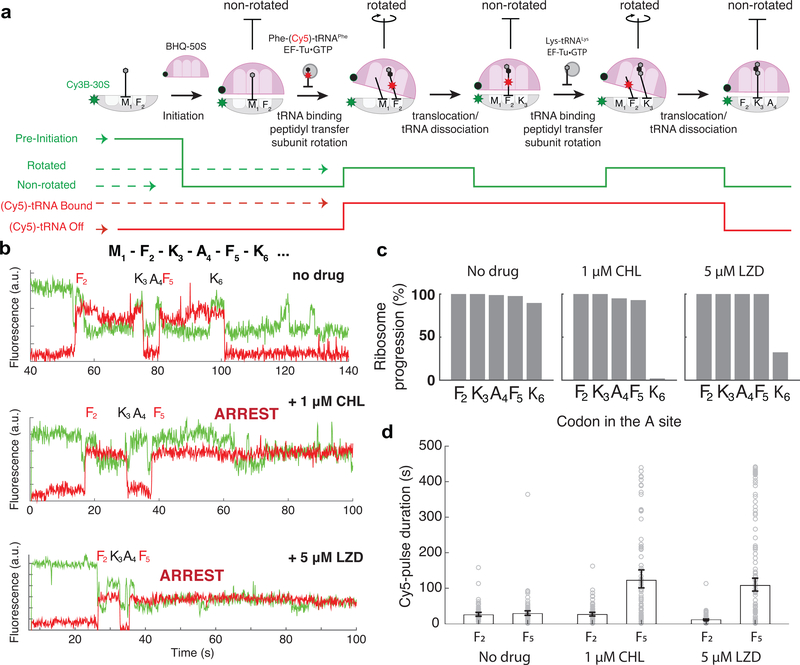
Figure 2. Monitoring the drug-induced translation arrest using smFRET-based assay.
a. Top: Diagram of smFRET-based assay to monitor ribosome structural changes coupled to translation elongation progression. Using Cy3B–BHQ-2 dye-quencher pair, non-rotated and rotated ribosome conformations are tracked. Binding of labeled specific tRNA (Phe-(Cy5)-tRNAPhe) is used to enhance fidelity of state transitions. Bottom: diagram of expected fluorescence intensities matching the structural states depicted immediately above. b. Representative traces for experiments without any antibiotics (similar results observed for n = 87, 100 and 139 for conditions “no drug”, “1μM CHL” and “5μM LZD”, respectively). c. Processivity of translation over the first six codons within the mRNA open reading frame at different conditions, measured as percentage of ribosomes that translated a particular codon over the entire population. d. Measurement of Cy5 pulse-durations from Phe-(Cy5)-tRNAPhe binding events at Phe codon 2 (F2) and Phe codon 5 (F5) for different conditions. Error bars represent 95% confidence interval from fitting the single-exponential distribution. Sample sizes for each conditions are identical in 2b-d.