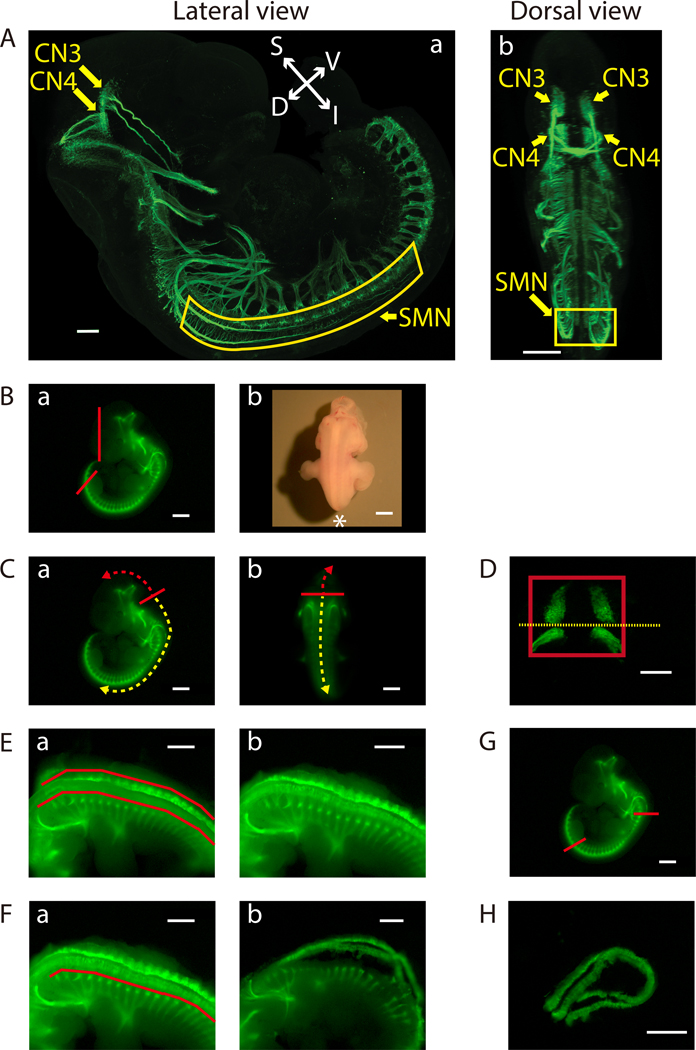
Figure 2: Dissection of the ventral midbrain and the cervical (C1) - lumbar (L2-L3) portion of the ventral spinal cord.
A) Lateral (a) and dorsal (b) views of GFP-positive motor neurons in an E11.5 IslMN:GFP transgenic mouse embryo under fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) illumination. A whole mount E11.5 embryo was prepared as previously described32 in order to make the embryo transparent. Subsequently, the embryo was analyzed by immunofluorescence labeling with anti-GFP staining (green). Images were captured under a confocal microscope. Scale bars: 200 μm (lateral view) and 400 μm (dorsal view). Abbreviations: S: superior; I: inferior; V: ventral; D: dorsal. B-H) Dissection steps highlighted on images of E11.5 ventral midbrain and ventral spinal cord tissues taken with an equipped camera under bright light (Bb) or FITC illumination using a fluorescence dissection stereomicroscope. Scale bars: 200 μm (D) and 1 mm (A-C, E-H). B) a) Remove the face and tail of the embryo by cutting along the red lines. b) Embryo positioned for dissection. Positioning of the front of the microscope is indicated by *. C) Cut along the solid red line in order to slit open the roof of the fourth ventricle [a) lateral view and b) dorsal view]. Use this opening to cut along the surface of the embryo dorsal to the brain (trajectory indicated by dashed red arrow). This will expose the tissue containing mesenchyme, CN3, and CN4, which can be lifted out of the cranium. For SMN dissection, insert forceps into the same opening between the fourth ventricle and its roof, then cut toward the caudal side of the embryo (trajectory indicated by dashed yellow arrow). D) Final view of the ventral midbrain containing bilateral GFP-positive CN3 and CN4 nuclei. The edges of the tissue are highlighted by a red rectangle. Cut along yellow dotted line to collect CN3 and CN4 nuclei separately, if desired. E) After opening the rest of the hindbrain and spinal cord, pinch off flapping dorsal tissues above the red lines on both sides with tweezers [a) before and b) after]. F) Bilaterally remove excess tissue ventral to the spinal cord along the red line [a) before and b) after]. G) Cut the ventral spinal cord at the two locations indicated by the red lines. On the rostral side, cut the floating ventral spinal cord transversely above C1 where the first GFP-positive anterior horn projects. Cut the caudal end of the spinal cord transversely at the upper boundary of the lower limb. Once these cuts are made, the cervical (C1) through lumbar (L2-L3) portion of the ventral spinal cord can be dissected away. H) Final view of the ventral spinal cord containing GFP-positive SMN columns.