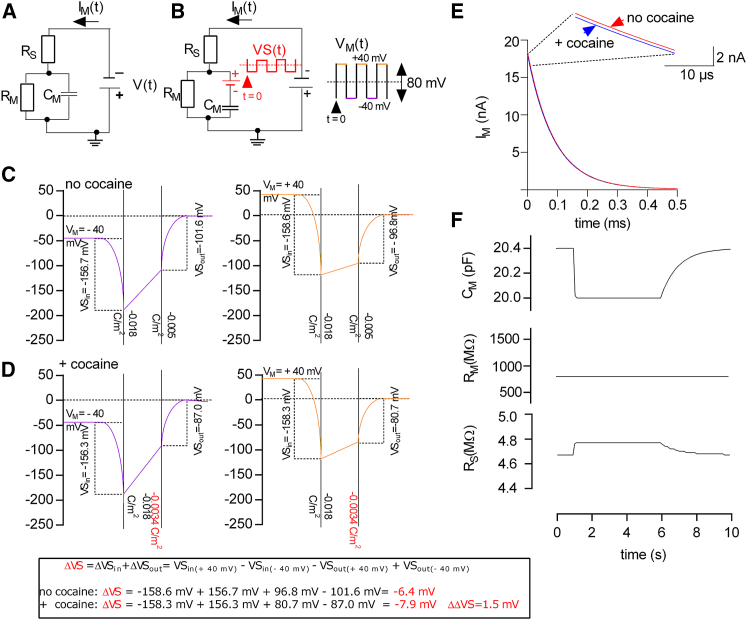
Figure 2.
The apparent change in membrane capacitance can be accounted for by an extended equivalent circuit of the cell. (A) Schematic representation of the minimal circuit of a cell is shown. (B) Shown is a schematic representation of an extended equivalent circuit of the cell; a battery (in red) was added to the minimal equivalent circuit shown in (A). The depicted voltage square-wave stimulus VM(t) was applied to the cell to elicit the recordings shown in Fig. 1A. VM was stepped from −40 to +40 mV in time increments of 5 ms. The resulting changes in voltage VS(t) at the added battery were calculated by utilizing the Gouy-Chapman model and are shown as red traces. (C) Shown is a voltage profile over the membrane in the absence of cocaine. The potential at the inner and outer surface was calculated utilizing the Gouy-Chapman model as adapted by (15). For the simulation, we assumed that both the inner and outer solution contained 150 mM NaCl. Initial surface charge densities for a HEK293 cell were taken from (16). The left- and right-hand panel in (B) show the voltage profile for voltage differences (VM) between the outer and inner bulk solution of −40 and +40 mV, respectively. (D) Voltage profile over the membrane in the assumed presence of a saturating concentration of cocaine is shown. The left and the right panel show the voltage profile at −40 and +40 mV, respectively. The potential at the membrane surfaces in (C) are different from that in (B). This is because in (C), the outer surface charge density was assumed to change to −0.0034 C/m2 as a consequence of cocaine binding. The inserted box at the bottom of (C) shows the calculation of the voltage step, which occurs at the added battery according to the Gouy-Chapman model. (E) Simulated current responses of a cell expressing SERT in the assumed absence (red trace) and presence (blue trace) of cocaine are shown. The inset shows that the current amplitude of the response in the absence of cocaine is slightly larger than in the presence of cocaine. (F) Simulated current responses were analyzed by employing the minimal equivalent circuit of the cell (A). This analysis misinterprets the change at the battery as a change in the other circuit parameters. The parameters that are most affected are RS and CM. To see this figure in color, go online.