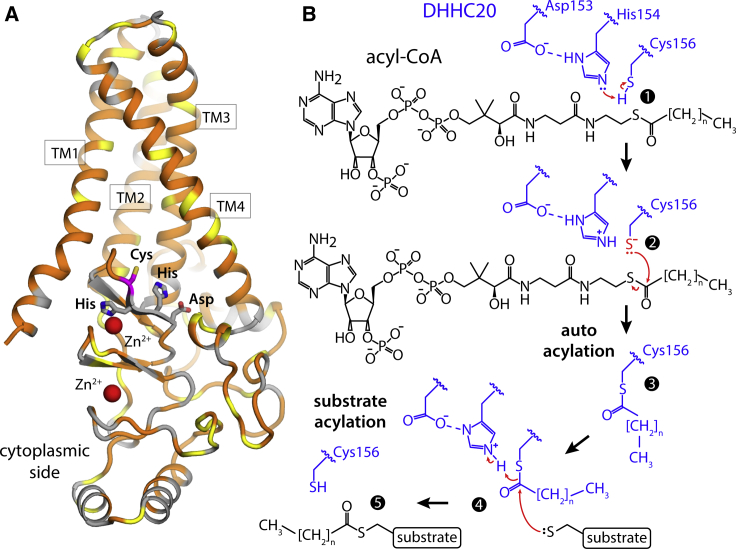
Figure 1.
Structure of human DHHC20 and proposed catalytic mechanism. (A) The existing crystal structure of hDHHC20 (PDB: 6BMN) is shown. The overall fold of the structure is represented with cartoons, indicating the four transmembrane spans (TM1–TM4). Hydrophobic and/or aromatic residues are colored in orange, serine and threonine residues in yellow, and others in gray. The side chains that define the catalytic site (Asp153-His154-His155-Cys156) are highlighted, as well as two structural Zn2+ ions. (B) Scheme for the hypothetical two-stage S-acylation reaction mediated by DHHC20: steps 1–3 make up the autoacylation stage, whereby an acyl-chain is linked to Cys156; in steps 4–5, this acyl-chain is transferred to a substrate. Red arrows indicate the proposed reaction pathway. His213, in TM4, lies within 5 Å of both Asp153 and His154, and might also be involved in this reaction (data not shown for clarity); its role might be to capture a proton initially bound to His154 before acyl-CoA recognition and at the onset of the autoacylation reaction described in (B). To see this figure in color, go online.