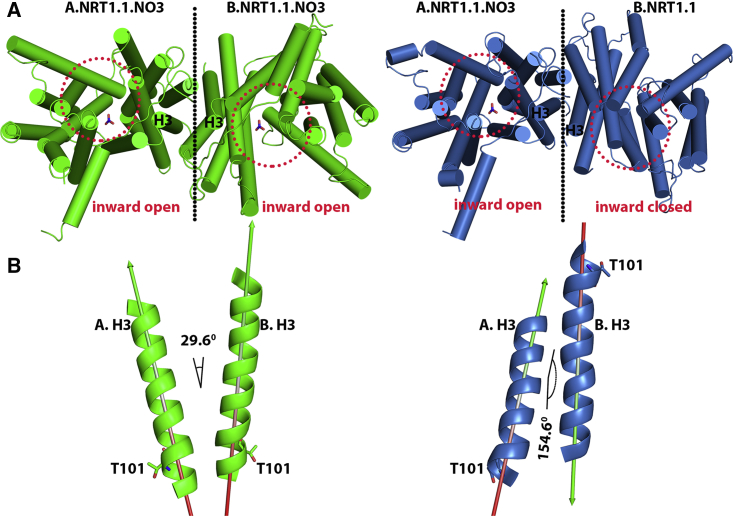
Figure 2.
In low nitrate concentration, nitrate-induced intermonomer rotational dynamics cause dimer decoupling and attenuation of nitrate transport through the monomer B. (A) Both the monomers are nitrate-bound and show an inward-open nitrate transport tunnel. In this case, the interface helices A.H3 and B.H3, in which the phosphorylation site T101 is located at the bottom, made the angle 29.6° with the same orientation. (B) In contrast, whereas nitrate is bound only on monomer A, there is large rotational dynamics of monomer B, in which the interface helices A.H3 and B.H3 show the opposite orientation with an angle of 154.6°. To see this figure in color, go online.