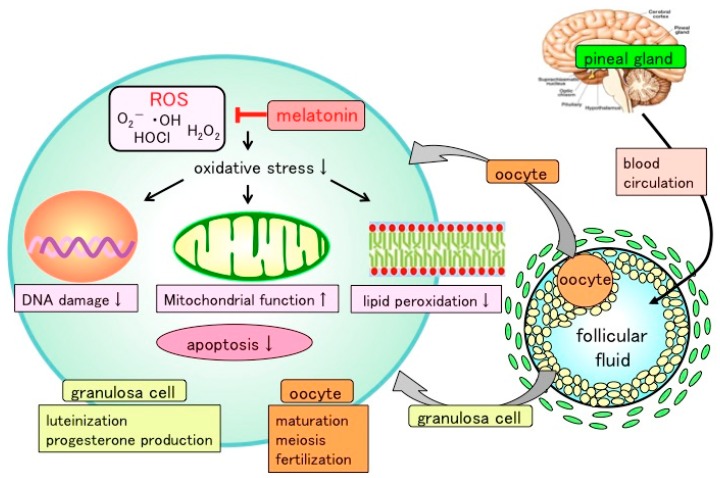
Figure 1.
Presumed action of melatonin in ovarian follicle. Melatonin, secreted by pineal gland, is taken up into the follicular fluid from the blood. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced within the follicles, especially during the ovulation process, are scavenged by melatonin. Excess amounts of ROS may be involved in oxidative stress of oocyte and granulosa cells. Melatonin reduces the oxidative-stress-induced DNA damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, lipid peroxidation, and apoptosis of granulosa cells, showing that melatonin protects these cells by reducing free radical damage of cellular components including nuclei, mitochondria, and plasma membranes. The balance between ROS and antioxidants (melatonin) within the follicle may be critical for oocyte maturation, meiosis, and luteinization of granulosa cells.