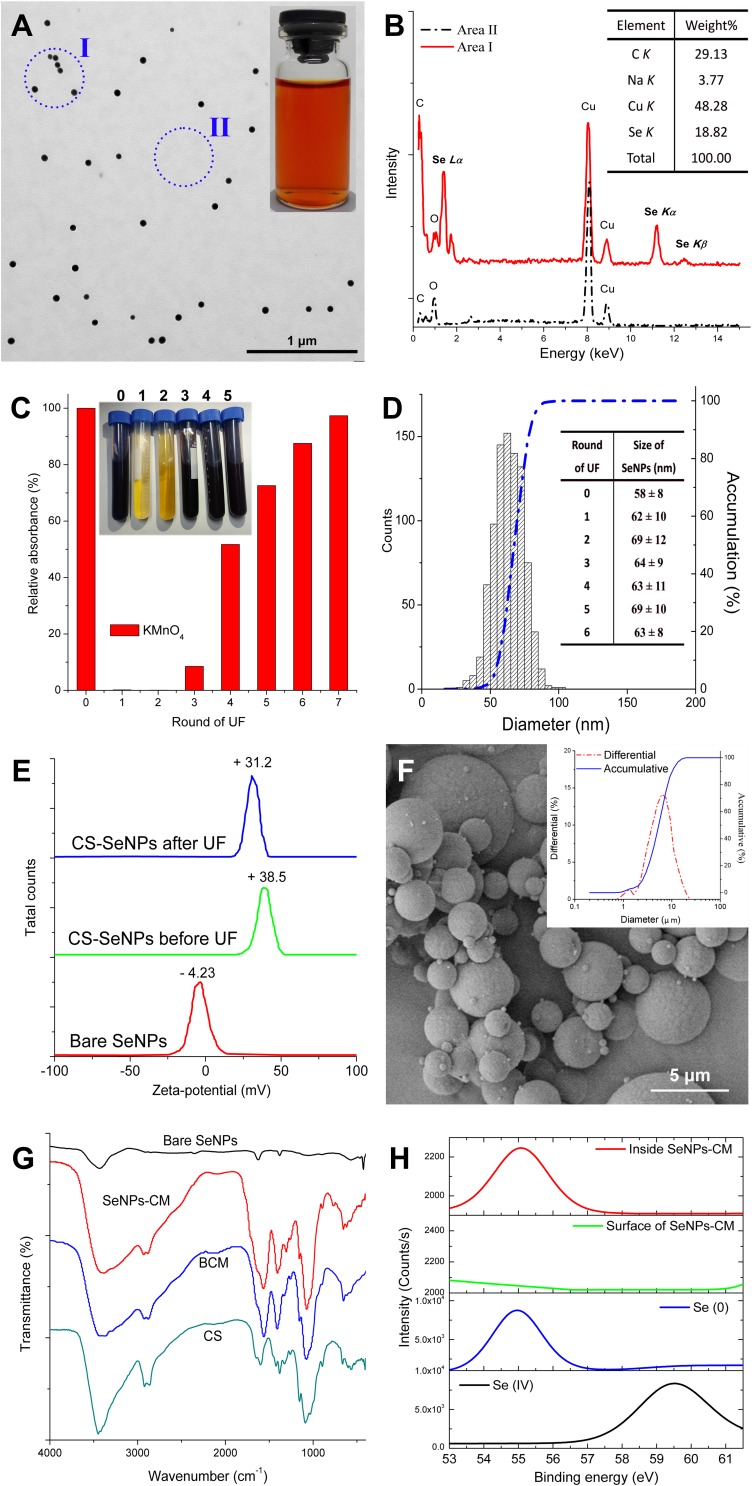
Figure 1.
The physicochemical properties of CS-SeNPs. (A) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image of CS-SeNPs and their appearance (inset). (B) Typical energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) spectra of CS-SeNPs (found at Area I, Panel (A) and their elemental composition (inset). (C) The absorbance (525 nm) of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) solution when coming across with UF filtrate and their appearance (inset). (D) The size distribution of CS-SeNPs measured basing on TEM results, and the influence of UF on the size of these nanoparticles (inset). (E) Zeta-potentials of bare SeNPs and CS-SeNPs (before or after 6 rounds of UF). (F) SEM image of SeNPs-CM and their size distribution (inset). (G) FTIR spectra of bare SeNPs, BCM and SeNPs-M. (H) Se 3d XPS patterns of Se (IV) (selenite or selenium dioxide), Se (0) (bare SeNPs or crystal Se) and SeNPs-CM, obtained with or without argon etching.