Figure 1.
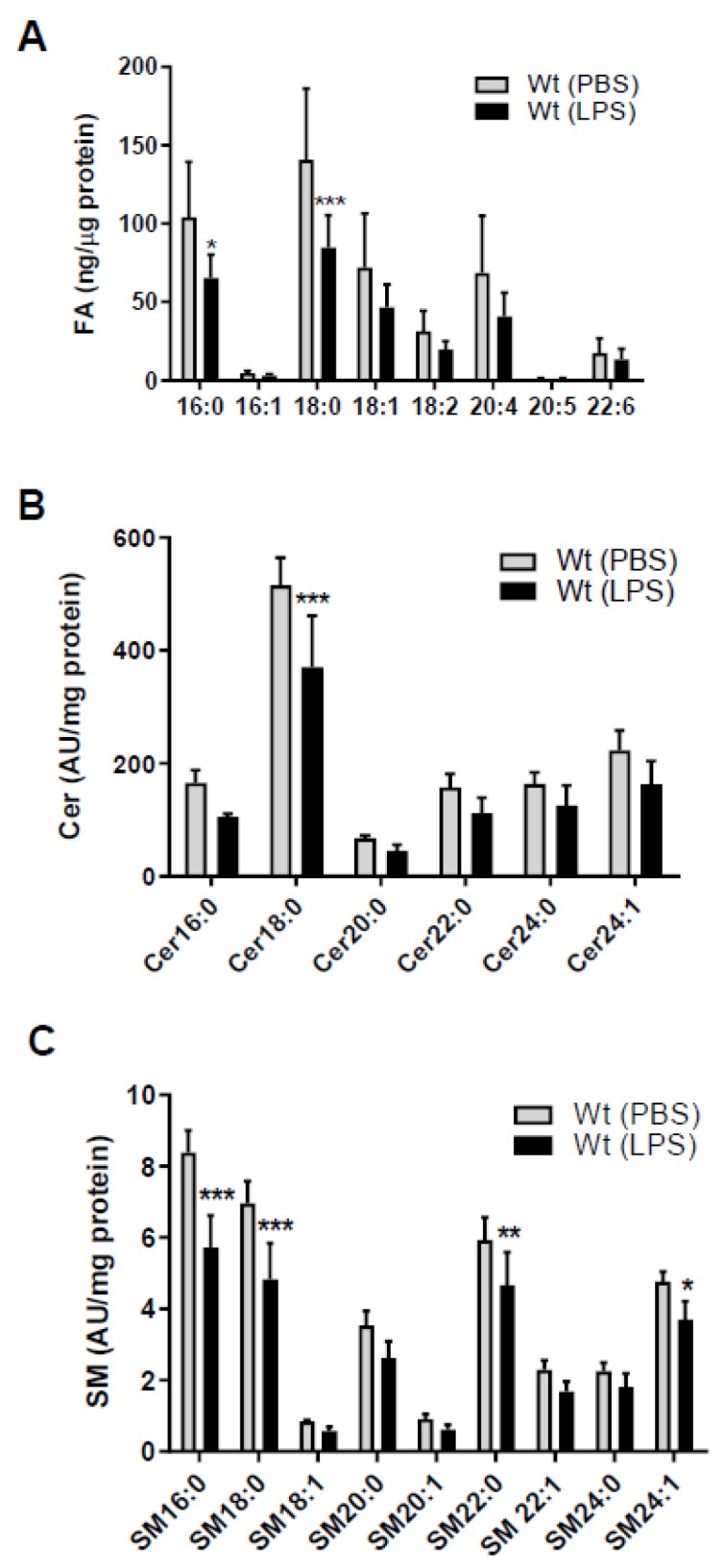
Peripheral lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration decreases fatty acid (FA), ceramide (Cer), and sphingomyelin (SM) content in brain microcapillaries of wild-type (wt) mice. Wt mice received a single i.p. injection of PBS (200 µL) or LPS in PBS (from Escherichia coli, 0111:B4 in PBS, 8.3 µg/g body weight) and were sacrificed 16 h after injection. (A) GC analysis of the total FA content of mouse brain microcapillaries (pooled from two brains per sample) as FA methylester derivatives. Significance was calculated by ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni correction. Data are shown as mean (n = 6–7) + SD. (B) Levels of Cer and (C) SM species in isolated brain microcapillaries (pooled from 3 brains per sample) were measured by LC-ESI-MS/MS. Cer and SM species are displayed on basis of their acyl chain composition. The values obtained were normalized to the internal standard and protein amount (arbitrary units (AU)/mg protein). Data are shown as mean (n = 5) + SD. Significance was calculated by ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni correction. *, p < 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001.
