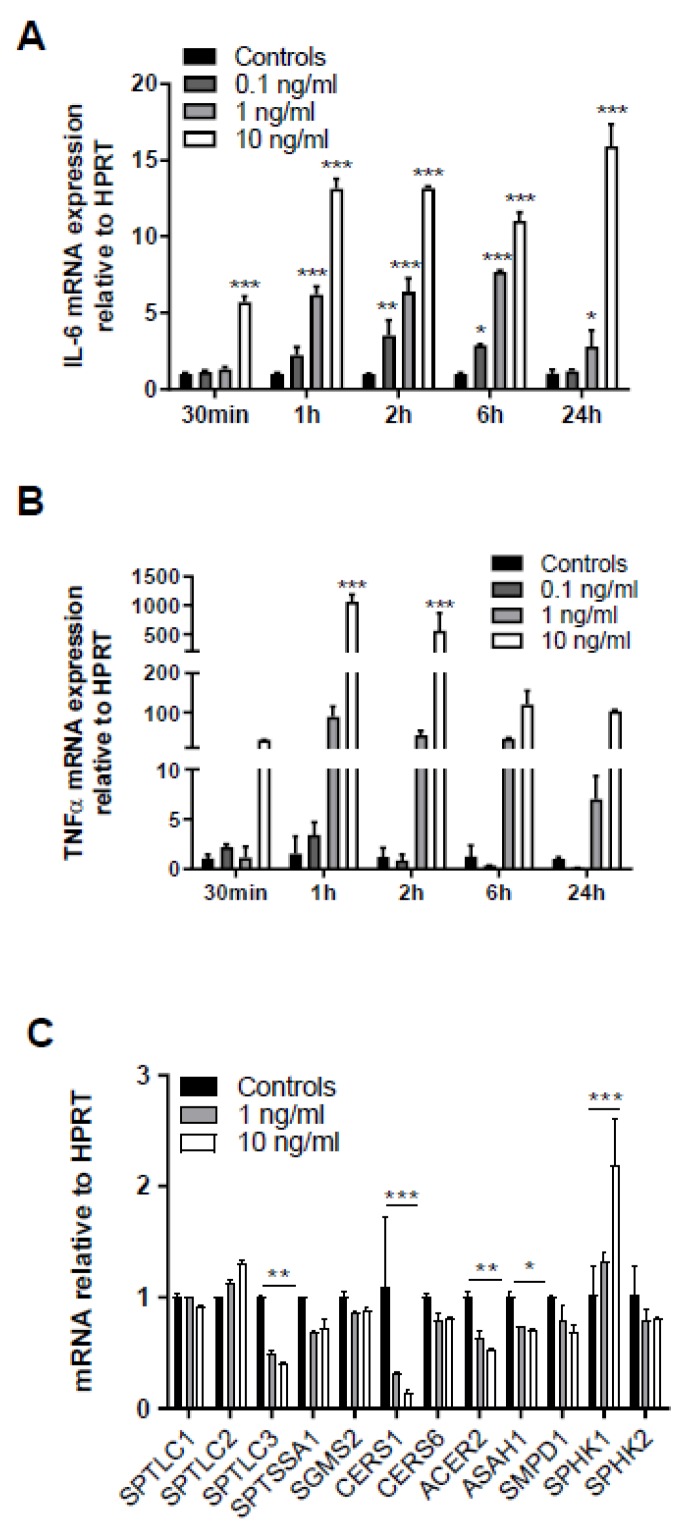
Figure 5.
Exogenous TNFα increases in cytokine synthesis and regulates expression of genes involved in sphingolipid metabolism. Serum-starved human brain endothelial (hCMEC/D3) cells were treated with the indicated rTNFα concentrations (0.1–10 ng) for the indicated times and gene expression of (A) IL-6 and (B) TNFα was evaluated by qPCR analysis. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT) was used as housekeeping gene. Data are shown as mean (n = 4) + SD. (C) hCMEC/D3 cells were incubated with 1 or 10 ng/mL TNFα for 2 h and expression of serine palmitoyltransferase 1-3 (SPTLC1-3), serine palmitoyltransferase small subunit A (SPTSSA1), sphingomyelin synthase 2 (SGMS2), ceramide synthase 1 and 6 (CerS1 and CerS6), alkaline ceramidase 2 (ACER2), acid ceramidase (ASAH1), sphingomyelinase 1 (SMPD1), and sphingosine kinase 1 and 2 (SPHK1 and 2) was evaluated by qPCR analysis. Data are shown as mean (n = 3) + SD. Expression was calculated using the 2−ddCt method. *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Significance was calculated by ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni correction.