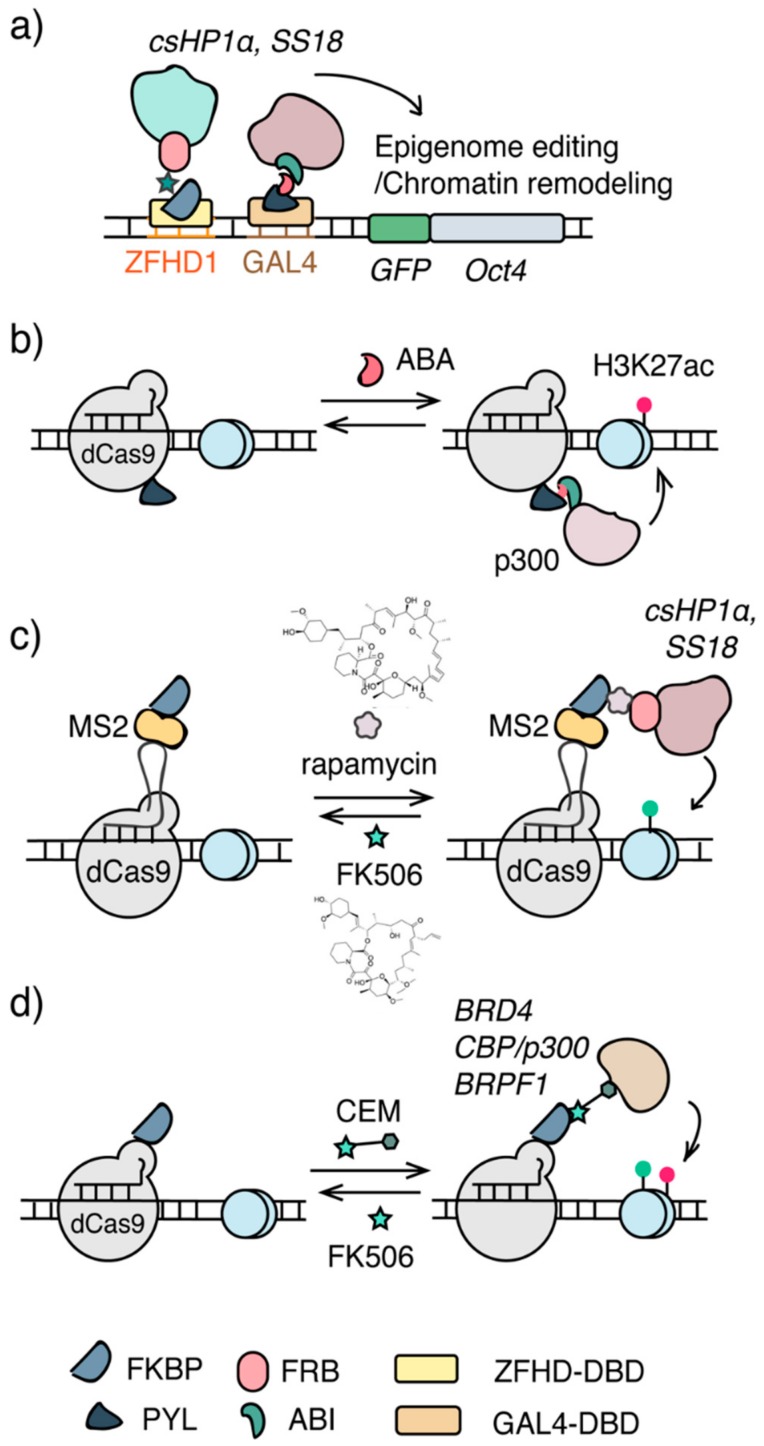
Figure 2.
Chemical inducible approaches for epigenome editing. (a) The Chromatin in vivo Assay (CiA) system. Arrays of DNA binding sites (e.g., GAL4, ZFHD1) were knocked-in upstream to the promoter of OCT4. Epigenome modifiers were recruited via DBD and CIP. (b) The CRISPR/dCas9-CIP integrated epigenome editing system. Acetyl transferase p300 core domain was recruited to specific genomic loci to install H3K27ac upon addition of ABA. (c) The FIRE-Cas9 system. CRISPR/dCas9 was combined with rapamycin CIP to recruit csHP1 and ss18/BAF for epigenome editing and chromatin remodeling. (d) Chemical epigenetic modifier (CEM), a bifunctional molecule containing an FKBP-binding molecule FK506 and a molecule recognizing a specific effector, recruits endogenous epigenome effectors to the targeted genomic locus for epigenome editing.