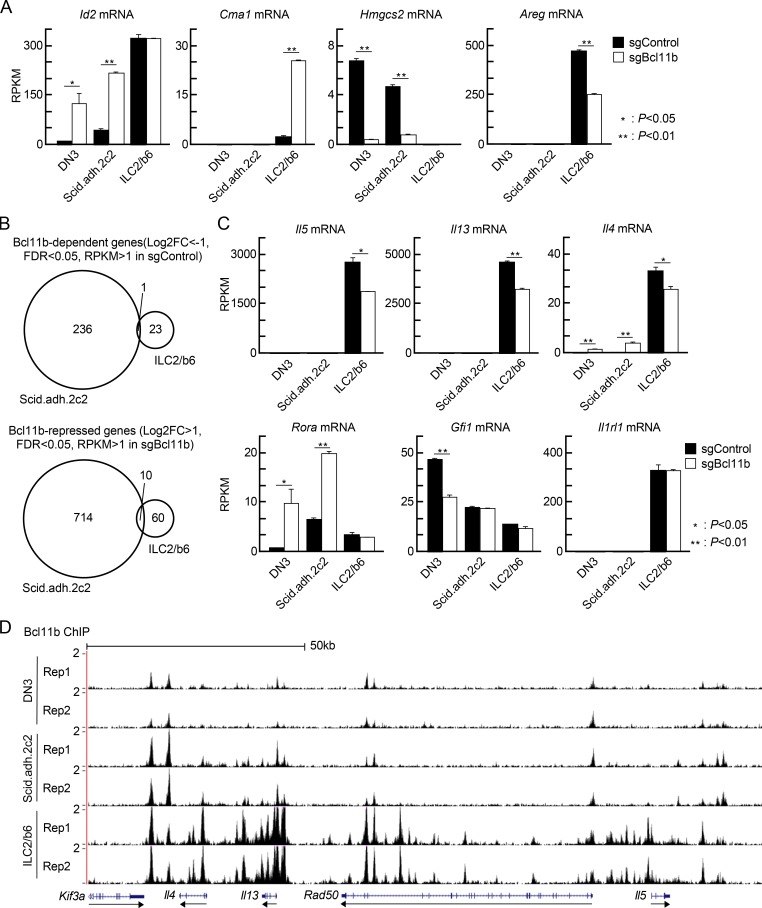
Figure 2.
Bcl11b controls distinct sets of genes in pro-T and ILC2 cells. (A) Scid.adh.2c2 and ILC2/b6 cells were first infected with Cas9-GFP, and GFP+ cells were expanded; then they were transduced with sgBcl11b-CFP retroviruses. 3 d after second infection, GFP+CFP+ cells were sorted and subjected to RNA-seq analysis. RPKM values for Id2, Cma1, Hmgcs2, and Areg in control and Bcl11b KO DN3 (Hosokawa et al., 2018a), Scid.adh.2c2, and ILC2/b6 cells are shown with SD. **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05 by Student’s t test. (B) Venn diagrams show the number of Bcl11b-dependent (log2 FC less than −1, FDR <0.05, RPKM >1 in sgControl, top) and Bcl11b-repressed (log2 FC >1, FDR <0.05, RPKM >1 in sgBcl11b, bottom) genes in Scid.ad.2c2 and ILC2/b6 cells. (C) RPKM values for Il5, Il13, Il4, Rora, Gfi1, and Il1rl1 in control and Bcl11b KO DN3, Scid.adh.2c2, and ILC2/b6 cells are shown with SD. **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05 by Student’s t test. Data for A–C are based on two replicate RNA-seq samples. (D) Two replicates of binding profiles of Bcl11b in DN3, Scid.adh.2c2, and ILC2/b6 cells around Th2 cytokine loci are shown.