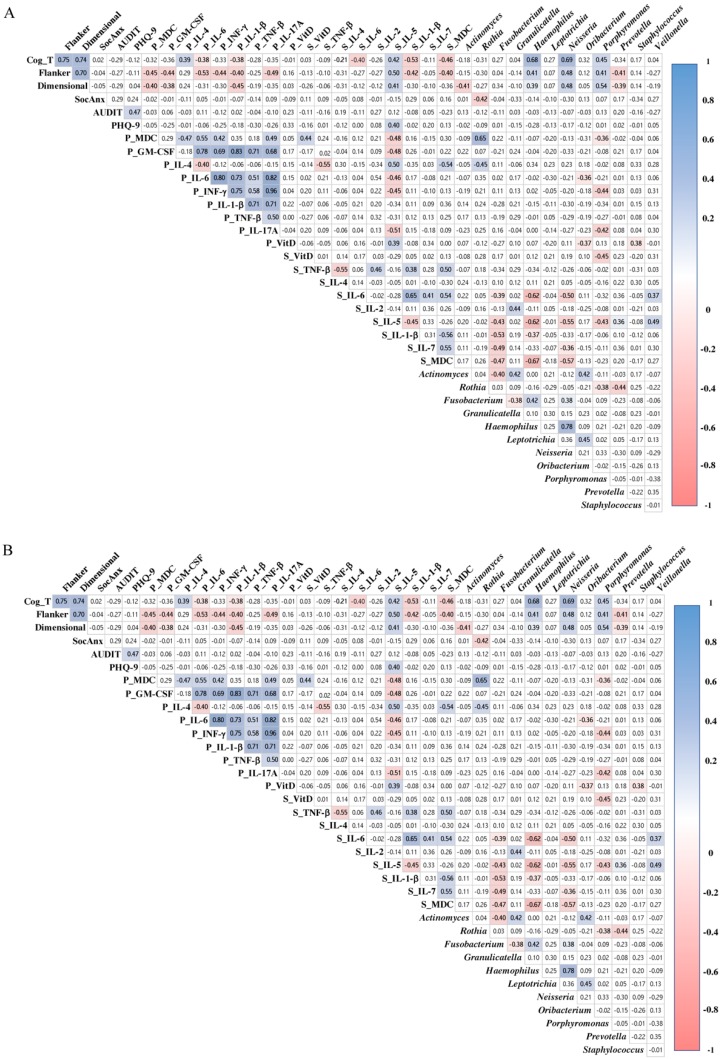
Figure 8.
Spearman Rho correlation among depression, social anxiety, executive functions, microbiota, and inflammatory markers in alcohol group (A), and control group (B). White squares indicate no significant association; blue squares indicate significant positive association; red squares indicate significant negative associations. Color intensity reflects stronger associations as determine by the correlation coefficient value (y-axis); p < 0.05. Cog_T: cognitive composite score of the NIH toolbox cognition battery; Flanker: Flanker inhibitory control and attention test; Dimensional: dimensional change card sort test; SocAnx: scores in the Leibowitz Social Anxiety Scale; AUDIT_T: total score in the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test; PHQ9: scores in the nine-item Patient Health Questionnaire; P_MDC: levels of macrophage-derived chemokine in plasma; P_GM-CSF: levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in plasma; P_VITD: levels of vitamin D in plasma; S_VITD: levels of vitamin D in saliva; S_MDC: levels of macrophage-derived chemokine in saliva. Other cytokines/chemokines expressed in plasma and saliva are: P_IL-4, P_IL-6, P_INF-γ, P_IL-1β, P_TNF-β, P_IL-17A, S_TNF-β, S_IL-6, S_IL-2, S_IL-5, S_IL-1β, and S_IL-7. The following are bacteria found in saliva: Actinomyces, Rothia, Fusobacterium, Granulicatella, Haemophilus, Leptotrichia, Neisseria, Oribacterium, Porphyromonas, Prevotella, Staphylococcus, and Veillonella.