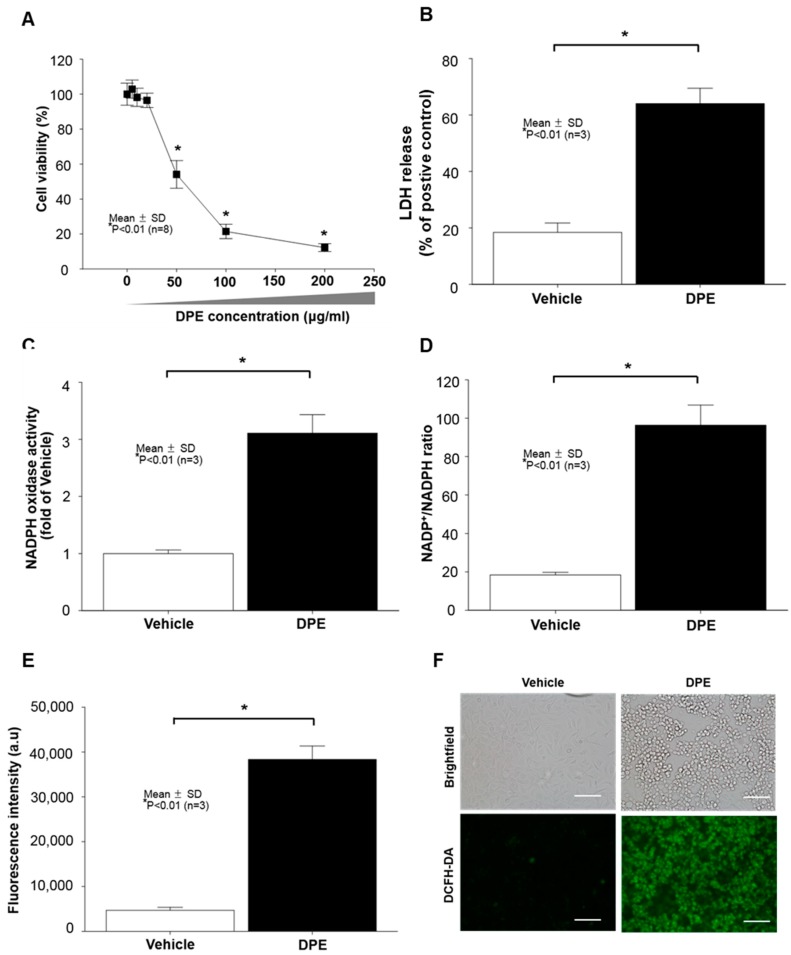
Figure 1.
Diesel particulate extract (DPE) induces keratinocyte (KC) apoptosis, paralleled by increased NADPH oxidase activity and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Human HaCaT KC were treated with DPE (100 μg/mL or as indicated) for 24 hrs. Cell viability was measured by a CCK-8 assay kit (A). Cell cytotoxicity was further determined by an LDH assay and results were expressed as LDH release compared to the positive control consisting of 0.1% SDS (yielding 100% LDH release) (B). In order to measure the levels of NADPH oxidation, cell membrane fractions were obtained as described in Materials and Methods. Activity of NAPDH oxidases was determined by either lucigenin chemiluminescence assay using N,N′-Dimethyl-9,9′-biacridinium dinitrate (C) or measuring the ratio of NADP+ to NADPH with LC-ESI-MS/MS (API 3200 QTRAP mass, AB/SCIEX) by multiple reaction monitoring mode (MRM) (D). Intercellular ROS production was determined by either a fluorospectrophotometer (E) or fluorescence microscopy (F) with the oxidant-sensing probe 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA). All values are mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was calculated using the unpaired Student’s t-test, and significance was defined as p < 0.01 vs. vehicle control (or untreated control). Bar = 500 μm.