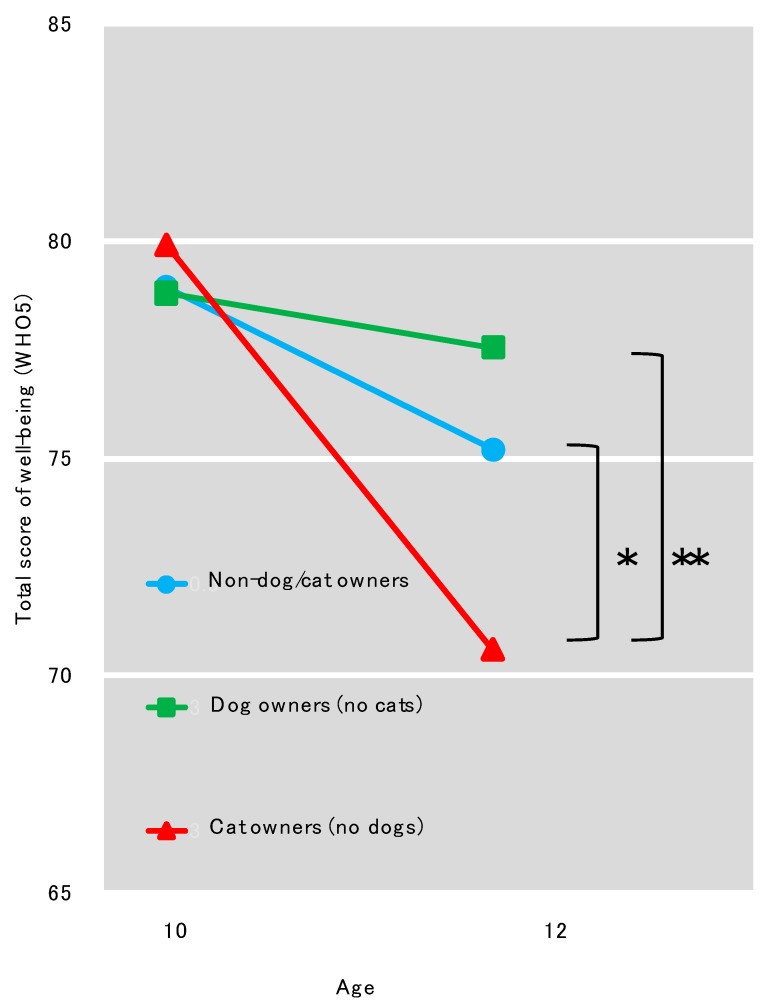
Figure 1.
Averages of well-being (WHO5) at ages 10 and 12 among non-dog/cat owners, dog owners, and cat owners (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). Two-way mixed-design analysis of variance (ANOVA) showed significant interaction of time points and owner types (F (2, 2572) = 6.78, p = 0.001). Simple main effect of owner types was not significant at age 10 (F (2, 2572) = 0.18, p = 0.835), but it was significant at age 12 (F (2, 2572) = 6.61, p = 0.001). Bonferroni adjustments were administered for multiple comparisons and found significant pairs at age 12 as follows: cat owners (owned no dogs) and non-dog/cat owners (p = 0.017) and cat owners (owned no dogs) and dog owners (owned no cats) (p = 0.001). Other pairs were not significant. The simple main effect of time points was significant in non-dog/cat owners (F = 85.55, p < 0.001) and cat owners (owned no dogs) (F = 26.21, p < 0.001) but not significant in dog owners (owned no cats) (F = 1.38, p = 0.240).