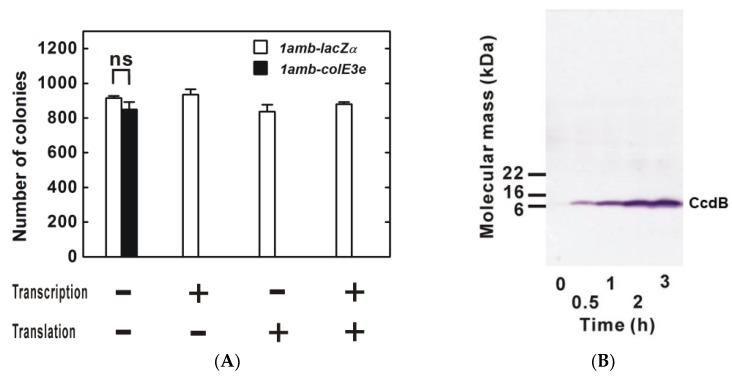
Figure 2.
Production of highly-toxic proteins using HYZEL. (A) Maintenance of ColE3e expression construct. The expression construct for the ColE3e gene, which contains a single amber stop codon insertion, was introduced into E. coli BL21-AI with another plasmid that constitutively expresses the specific UaaRS for ZK and its cognate tRNACUA. A V5-LacZ with a gene containing an amber stop codon insertion was used as non-toxic protein control. Leakage expression of ColE3e killed the host bacteria using single repression at the transcriptional or translational level. In contrast, the host bacteria survived in dual transcriptional-translational repression. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. of three biological replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using single-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) with an α of 0.05 (ns, not significant). (B) Production of the DNA gyrase inhibitor, CcdB. CcdB with a V5 epitope tag added at the N-terminus was produced using HYZEL. An amber stop codon was inserted next to the translation start codon in the V5 epitope tag. The V5-CcdB expression construct driven by T7RNP was cotransformed into BL21-AI with a plasmid that constitutively expressed the specific UaaRS for IY and its cognate tRNACUA. Bacteria carrying these plasmids were cultured overnight in LB medium containing D-glucose for catabolite repression against PBAD-araC/O, which regulates T7RNP gene expression. V5-CcdB production was induced by changing the medium containing IY, L-arabinose and IPTG. V5-CcdB production was shown by western blot using an anti-V5 antibody. Time after the medium change is shown below the photo.