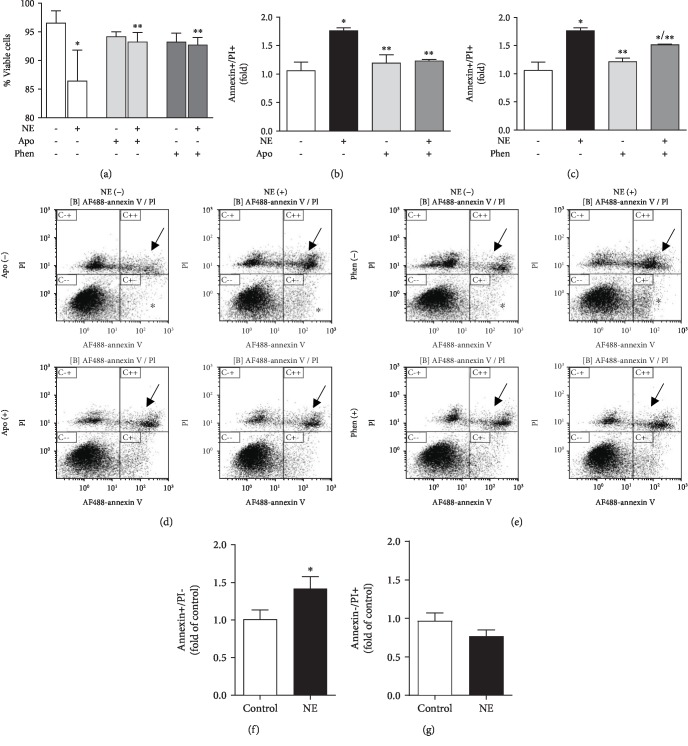
Figure 4.
Norepinephrine induces RLMEC death via ROS production and α1-adrenoceptor-mediated pathways. To assess the role of reactive oxygen species and α1-adrenoceptors in NE-induced cells death, RLMEC were treated with apocynin (Apo) and phentolamine (Phen) for 30 minutes before stimulation with NE (5 ng/mL) for 24 h. (a) NE reduced cell viability as assessed by trypan blue, an effect inhibited by Apo and Phen. (b). NE induces cell death as it increases the amount of annexin+/PI+ cells, an effect is abolished by Apo. (c). Phen partly inhibits NE-induced cell death. (d, e) Representative flow cytometry charts evidencing that NE increases the number of annexin+/PI+ cells (arrows) and the number of annexin-positive cells (stars); apocynin reduces the number of annexin+/PI+ cells to control levels, and Phen decreased the number of annexin+/PI+cells in 25%. (f) Bar graph indicating that NE increases the number of annexin+/PI- cells. (g) Bar graph indicating that NE does not alter the number of annexin-/PI+ cells. ∗p < 0.05vs. control, ∗∗p < 0.05vs. NE; N ≥ 4/group.