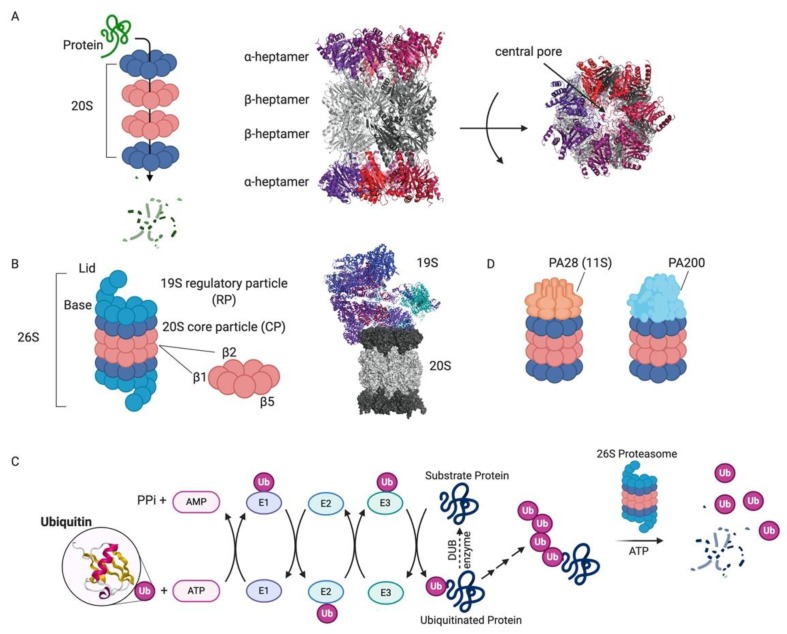
Figure 1.
Proteasome and ubiquitin-mediated degradation [85]. (A) Schematic of substrate protein degradation by passage through the central pore of the four stacked heptameric rings that comprise the 20S proteasome (left). The X-ray crystal structure of the yeast 20S proteasome (PDB 1RYP) shows the two capping α-heptameric rings (red/violet) and the middle two β-heptamers (grey; middle). The central pore through which substrates are threaded is indicated in the top view (right). (B) The 26S proteasome is the central component of the UPS. A cartoon depiction of the components of the 26S proteasome highlights the lid and base of the 19S RP in addition to the DUB Rpn11 and the catalytic β-rings (left). The cryo-EM structure of the human 26S proteasome (PDB 6MSB) shows the structure of the 26S proteasome in a state competent for ubiquitinated substrate engagement. (C) Schematic of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (ubiquitin PDB 1UBQ). (D) Schematic of alternative 20S proteasome complexes with a heptameric PA28 cap or a monomeric PA200 cap.