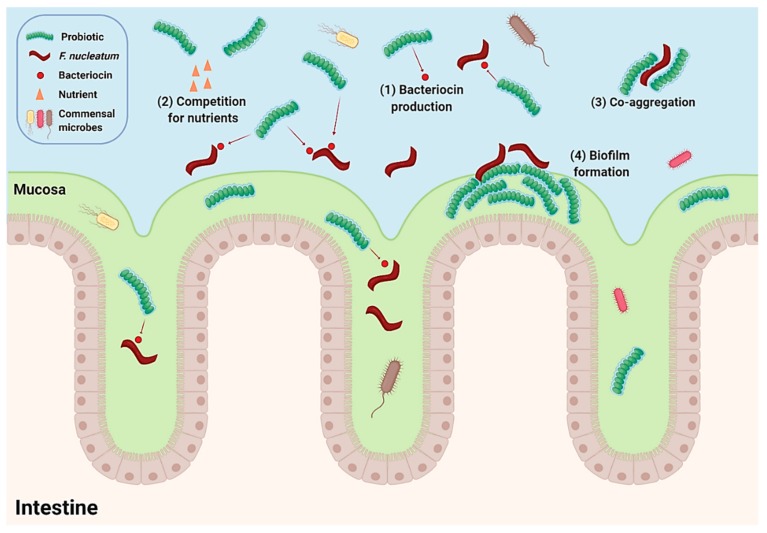
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanism of action by which probiotic supplementation may decrease the risk of developing colon cancer by inhibiting F. nucleatum through (1) bacteriocin production, (2) competition for nutrients, (3) co-aggregation, and (4) competitive exclusion through biofilm formation. This figure was Created with BioRender.