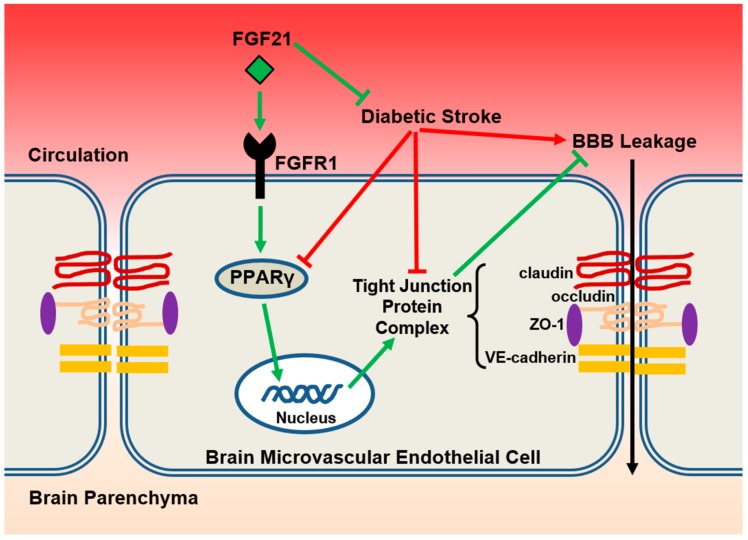
Figure 6.
The proposed model. In the setting of diabetic ischemic stroke, brain microvascular endothelial cells suffer more severe damage, including exacerbated reduction of PPARγ activity and tight junction protein expressions, and subsequently augmented BBB leakage. Exogenous administration of rFGF21 exerts BBB-protective effects through FGFR1-mediated elevation of PPARγ activity and upregulation of tight junction protein expressions and eventually mitigates the poststroke BBB permeability in the context of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).