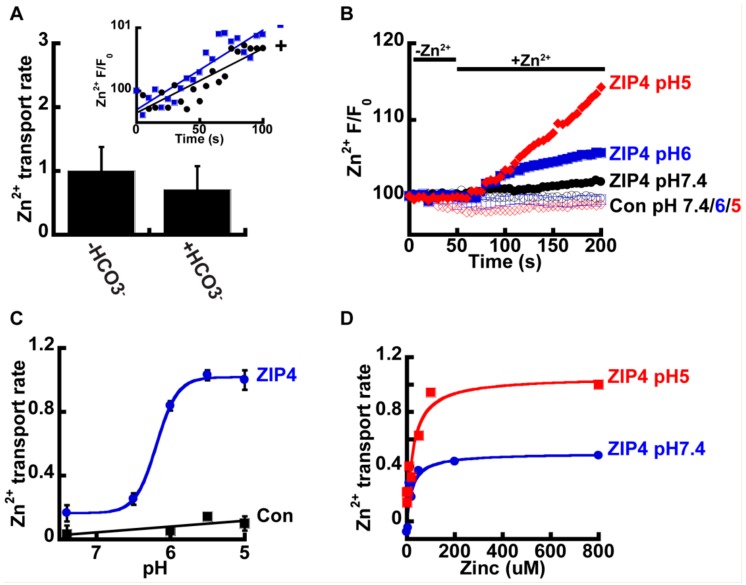
Figure 2.
ZIP4-mediated Zn2+ transport is pH dependent. (A) HCO3− has no effect on Zn2+ uptake. HEK293-T cells transfected with ZIP4 were loaded with 1 µM Fluozin-3AM and loaded with 50 µM Zn2+ in HEPES buffered Ringer’s solution (blue, in inset) or 20 mM NaHCO3− buffered Ringer’s solution (black, in inset) N ≥ 3. Normalized Zn2+ uptake rates in the presence or absence of HCO3− and is shown in the bar graph. (B) Representative traces of Zn2+ uptake, in HEK293-T cells, transfected with an empty control vector (empty symbols) or mZIP4 (full symbols) that were applied in Ringer’s solution at different pH levels, as indicated. (C) Normalized rates of Zn2+ uptake (compared to the rate of transport by mZIP4 at pH 5) by cells expressing either mZIP4 or a control vector N ≥ 5. Curve is a Michaelis Menten fit. (D) Rates of Zn2+ uptake, in HEK293-T cells expressing ZIP4, at pH 7.4 (blue) and pH 5 (red), at the indicated zn2+ concentrations (0–800 µM). Curve is a Michaelis Menten fit N ≥ 4.