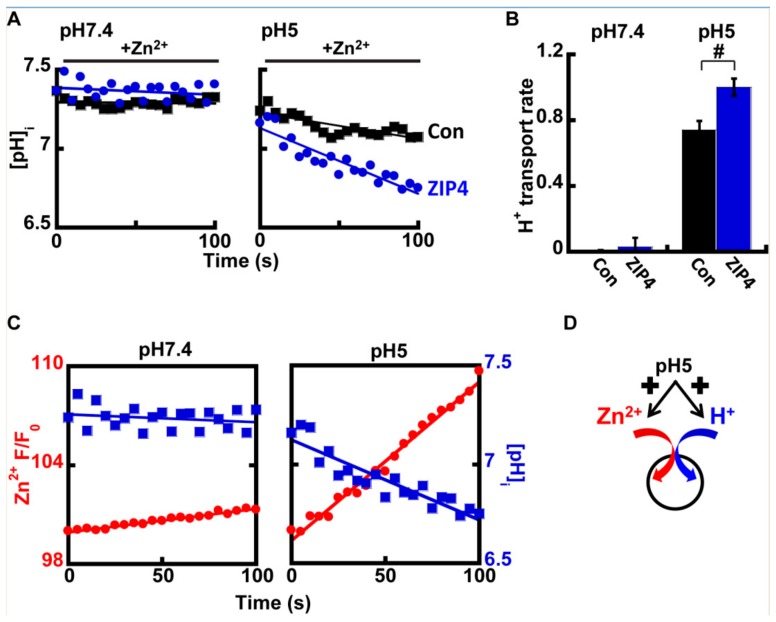
Figure 4.
ZIP4 mediates H+ coupled Zn2+ transport. (A) Representative traces of HEK293-T cells transfected with ZIP4 (blue) or a control vector (black), loaded with 1 µM BCECF-AM, and monitored for cytoplasmic pH changes at pH 7.4 (left) or pH 5 (right), following the addition of 50 µM Zn2+. (B) Normalized H+ transport rates recorded from control (black) or ZIP4 (blue) expressing cells, in the presence of 50 µM Zn2+ in the extracellular solution N ≥ 5. (C) Representative traces of Zn2+ (red) and H+ transport (blue), recorded with Fluozin-3AM and BCECF-AM accordingly. Note that H+ uptake is parallel to Zn2+ uptake. (D) Illustration of the suggested mechanisms of ZIP4. In (B), # is p ≤ 0.05 between control cells and cells expressing ZIP4 at pH 5.