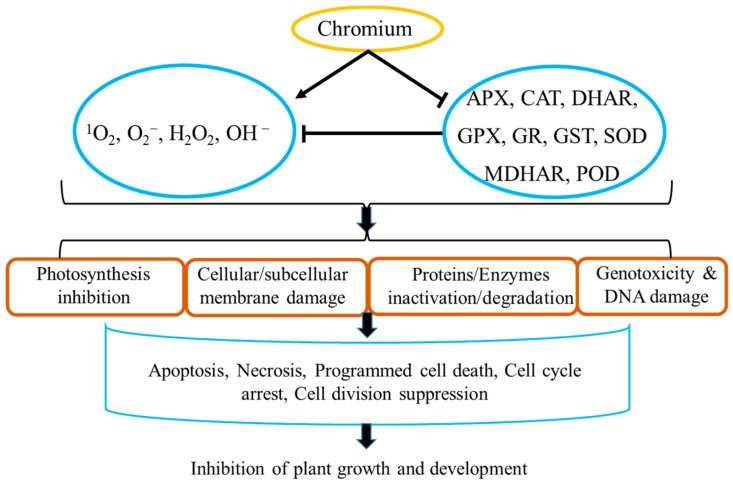
Figure 1.
Cr(VI)-induced ROS mediated alteration in plants: Cr(VI)-induces ROS accumulation by suppressing enzymatic antioxidant system, which damages cellular and subcellular membranes; induces ultrastructural changes in cell organelles such as mitochondria, plastids, and thylakoids; inhibits protein and enzymes at transcriptional or post-transcriptional level as well as degrades various enzymes and proteins; and DNA damages. All of these alterations inhibit photosynthesis and trigger and enhance necrosis, apoptosis, and programmed cell death, and significantly inhibit plant growth and development. Superoxide (O2−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl ion (HO−), and singlet oxygen (1O2). Ascorbate peroxidase (APX), catalase (CAT, dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione S-transferase (GST), monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR), peroxidase (POD), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). T-bars represent inhibition or suppression of the target, arrows represent promotion or upregulation of the target, and bold arrows represent the ultimate downstream result or impact of the process.