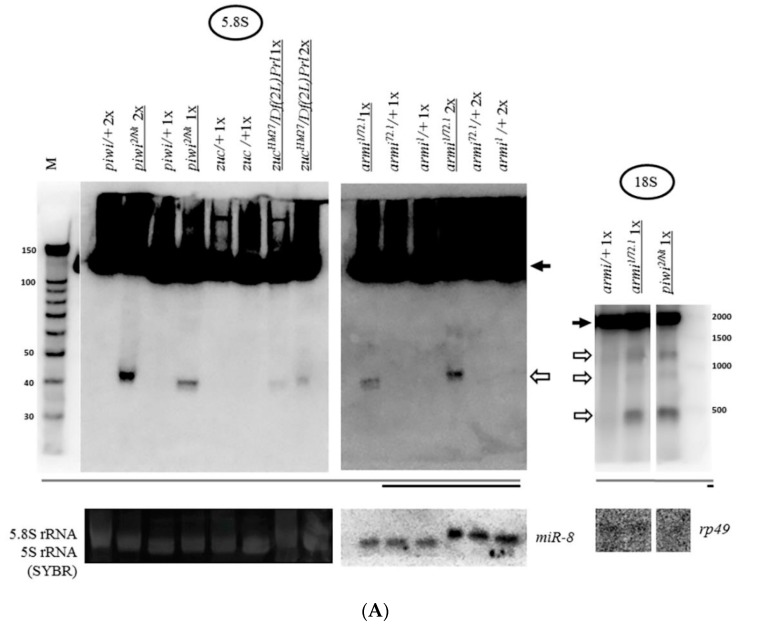
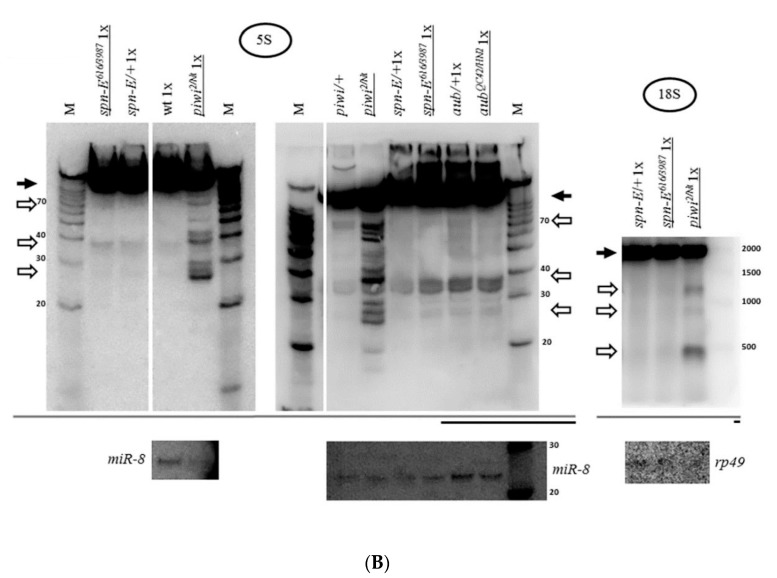
Figure 3.
Mutations in other primary piRNA processing components, but not ping-pong components of the piRNA pathway, cause a significant accumulation of rRNAs fragments: (A) Effects of mutations in zuc and armi of primary piRNA processing. The fragments significantly accumulate in the transheterozygous zucHM27/Df(2L)Prl ovaries (exemplified by 5.8S rRNA on the left) and armi1/72.1 ovaries (exemplified by 5.8S rRNA in the middle and 18S rRNA on the right). Fragments are designated by white arrows, mature rRNAs by black arrows; (B) Effects of mutations in aub and spn-E of ping-pong amplification. The fragments do not significantly accumulate in transheterozygous spn-E616/3987 ovaries (exemplified by 5S rRNA on the left and in the middle and 18S rRNA on the right) and aubQC42/HN2 ovaries (exemplified by 5S rRNA in the middle). Equal amounts of RNA were loaded on lanes of controls and mutants to be compared in each blot.