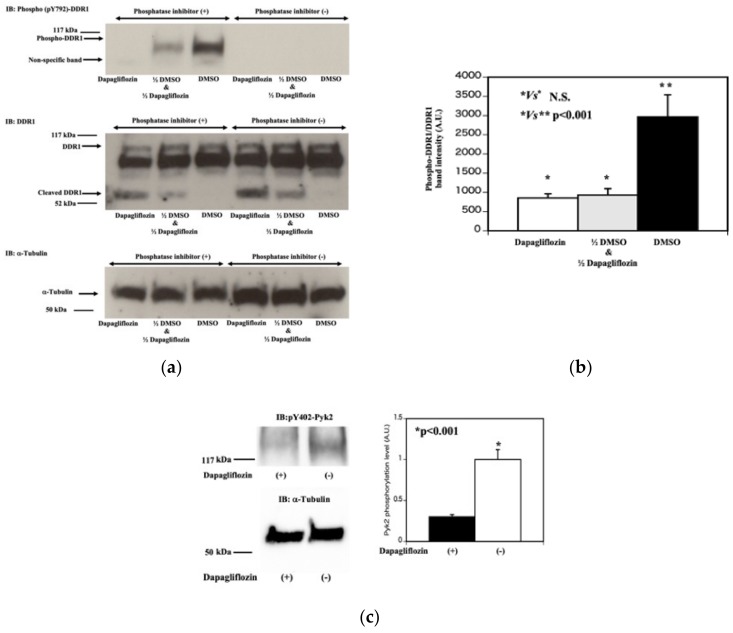
Figure 6.
Dapagliflozin increases tyrosine phosphatase activity that reduces DDR1 dephosphorylation. (a) DDR1 tyrosine phosphorylation. HCT116 cells were treated with vehicle (DMSO) or 0.5 mM dapagliflozin for 20 min. The cells were extracted in buffer with (+, 1–3 lanes from the most left lane) and without (−, 4–6 lanes from the most left lane) the phosphatase inhibitors (Sodium vanadate, Sodium pyrophosphate, Sodium Fluoride). Fifty microliters of lysate from DMSO treated HCT116 cells was mixed with 50 μL lysate from dapagliflozin treated HCT116 cells and incubated for 30 min at room temperature (labeled as 1/2 DMSO and 1/2 Dapagliflozin, the second lane from the most left lane in the left upper panel). In parallel, 100 μL lysate of DMSO treated HCT116 cells (the third lane from the left lane in the upper left panel) and 100 μL lysate of dapagliflozin treated HCT116 cells (the third lane from the left lane in the left upper panel) were incubated for 30 min at room temperature. Each lysate was run on SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membrane, and subjected to western blot using a pY792-DDR1 antibody (top panel), the 598 G antibody (middle panel) and α-tubulin (bottom panel). (b) Estimation of DDR1 tyrosine phosphorylation. Quantification of the DDR1 phosphorylation was determined by dividing the band intensity of the pY792-DDR1 antibody signal by the 598 G antibody full length DDR1 signal. (n = 3, * p Not significant, ** p < 0.001). (c) Effect of dapagliflozin on downstream of DDR1 signal pathway. HCT116 cells were treated with vehicle (−) or 2.0 mM dapagliflozin (+) for 20 min. Cell extracts were then immunoblotted for pY402-Pyk2 and α-tubulin. Quantification of pY402-Pyk2 relativeα-tubulin is presented in the bar graph (on the right side). (n = 3, p < 0.001).