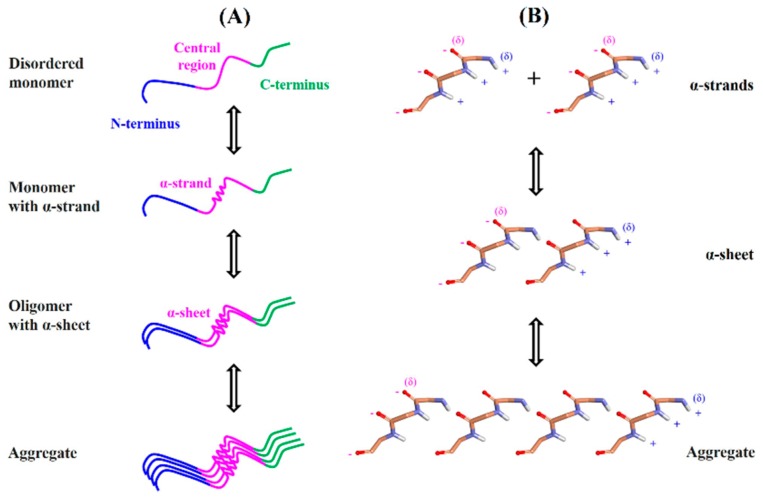
Figure 5.
Proposed aggregation mechanism. (A) Schematic representation showing α-strand/ α-sheet formation during Aβ1–42 aggregation process. N-terminal, central region, and C-terminal are indicated by blue, pink, and green colors, respectively. Central region (residues 24–26) of the monomer adopts the α-strand conformation occasionally. Hydrogen bonding between the α-strands leads to the formation of α-sheet structure in the oligomers. The α-sheet structure acts as a nucleus that initiates the aggregation process. Elongation of nucleus through the incorporation of further Aβ1–42 molecules form a mature fibril. (B) Alignment of carbonyl and amino groups generates two complementarily charged interfaces in the α-sheet structure. Attractive forces between the interfaces with opposite charges facilitate the aggregation of Aβ1–42. Negative and positive partial charges on the interface are shown by red and blue colors, respectively.